Actions to increase students' motivations for physical education
Фотографии:
ˑ:
PhD, Associate Professor O.P. Kokoulina1
N.E. Kopylova1
N.G. Efremova1
V.A. Zaitsev1
1Plekhanov Russian University of Economics, Moscow
Keywords: physical education, competency, socio-biological and psychophysical basics, physical education teacher's functions, personal physical culture.
Background. One of the key provisions of the Federal Law “On Physical Culture and Sports in the Russian Federation” gives a high priority to the socio-humanitarian dimension of the physical education service provided by the national education system, the provision being further spelled out in the relevant regulations of the Ministry of Education and Science of Russia. Based on the set of the above regulatory documents, we may define the mission of the academic physical education as the personal physical culture building to make the individual fit for future professional responsibilities and knowledgeable, among other things, in the socio-biological and psychophysical basics of intellectual labour.
The present demographical development concept of the Russian Federation makes an emphasis, among its other priorities in the people’s health improvement domain, on the initiatives to secure progress of the national physical culture and sports sector and offer health improvement leisure-time opportunities to the young generation. It should be mentioned, however, that the young people’s health may be viewed as an aggregate social individual portrait largely determined by a variety of subjective and objective social impacts and individual traits of each person.
Objective of the study was to analyse the ways to build up the current motivations of the Moscow university students for the academic physical education.
Methods and structure of the study. The study included a questionnaire survey (as of 2017) of the first-to-fourth year Moscow university students, with more than 200 students being subject to the survey. The survey data were processed and analysed by the Physical Education Department faculty.
Study results and discussion. The questionnaire survey data (see Table 1 hereunder), with the subjects’ interest in physical culture rated on a 10-point scale, show the interest clearly sagging with age – that may be due to the actual quality of the current metropolitan academic physical education service.
Table 1. Students’ interest in academic physical culture and sports, %
|
Interest rate |
Academic year |
|||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
|
High |
25,7 |
21,8 |
18,3 |
17,5 |
|
Above average |
20,3 |
19,6 |
16,6 |
16,8 |
|
Average |
19,7 |
20,4 |
21,5 |
20,0 |
|
Below average |
15,9 |
15,8 |
14,7 |
13,4 |
|
Low |
9,3 |
10,8 |
12,2 |
12,9 |
|
None |
9,1 |
11,6 |
16,7 |
19,4 |
The current shortage of theoretical and practical knowledge and operational components in the curricula giving the means for creative health building activity makes it virtually impossible for the students neither to develop due physical culture among the other academic competences nor contribute it to the national physical culture on the whole.
None of the existing textbooks duly covers the personal physical culture building theories and practical technologies. Therefore, there is still some contradiction between the core idea of the State Education Standard for the Physical Education discipline regulating every education stage (i.e. the personal physical culture building process) and the shortage of the relevant professional and educational competences in the physical education specialists; and such an awkward situation heavily complicates the education process. This is the reason why many educators opt for the health improvement domain of physical education and, partially, the educational and cultural domains (limited by motor skills mastering and physical qualities development aspects), albeit the following aspects of the process are still inadequately addressed:
– Values, cultural and world outlook building functions of physical education as an academic discipline;
– Competence and practical ability developing component of the subject intended to lay a practical methodological basis for the individual physical progress and sporting activity and mobilise the individual creative potential to develop independence and proficiency in this physical education domain; and
– High integrity of the individual physical culture formation process with its key elements being duly harmonised.
On the whole the academic youth health problem in the context of the academic physical education may be described as multisided in at least social, economical, professional and individual aspects. The firm and active attitudes and competent choice of the applicable physical education and sporting methods and tools for the healthy lifestyle building purposes largely determine success of the individual physical culture development process. In other words, the academic physical education with ample time assigned to the discipline in the curriculum must perform a variety of research, informational, cultural, intellectually developing, creative, spiritual progress securing and other personality building functions in the process. In addition, it must be considered an integral part of the academic education and cultural process to maintain high intellectual and physical working capacity in the trainees and help them develop due motivations and values for the individual physical progress and meet their natural demand for different forms of physical and sporting activity.
It is the faculty‘s competency that is one of the key conditions for success of the academic physical culture building in the young peoples’ subcultures. We grouped and ranked the specialists’ competences to evaluate and analyse the current competency of the subjects: see Figure 1.
The valuations were made by an expert team including 29 leading academic physical education and sport specialists of Moscow city. The expert valuations were complemented by the self-ratings of the subjects.
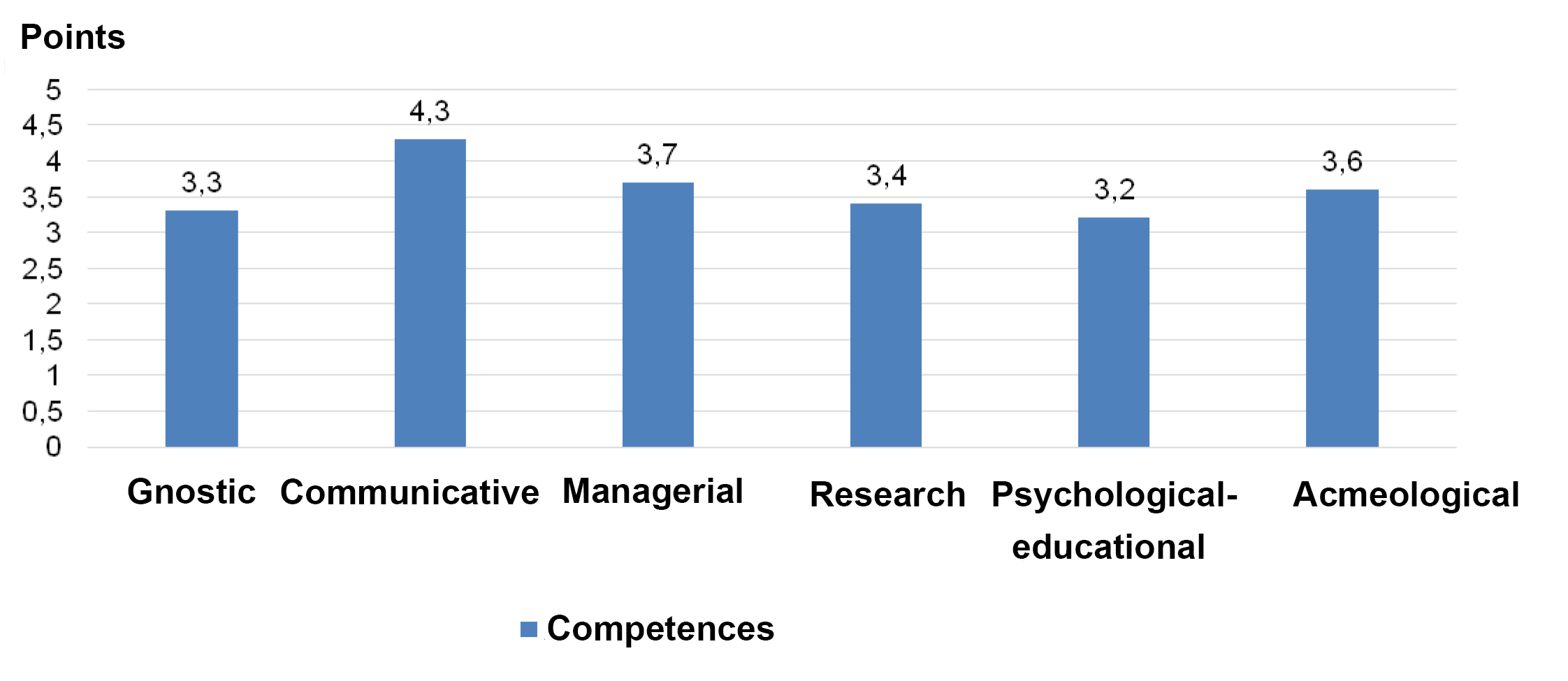
Figure 1. Valuations of the academic educators and trainers’ competences
Mean arithmetic values were used to calculate the final rankings of the specialists’ professional competences (see Figure 2) as follows:
- Critical level: 2-3 points;
- Average level: 3.1 to 3.8 points;
- Adequate level: 3.9 to 4.4 points; and
- Perfect level: 4.5 to 5 points.
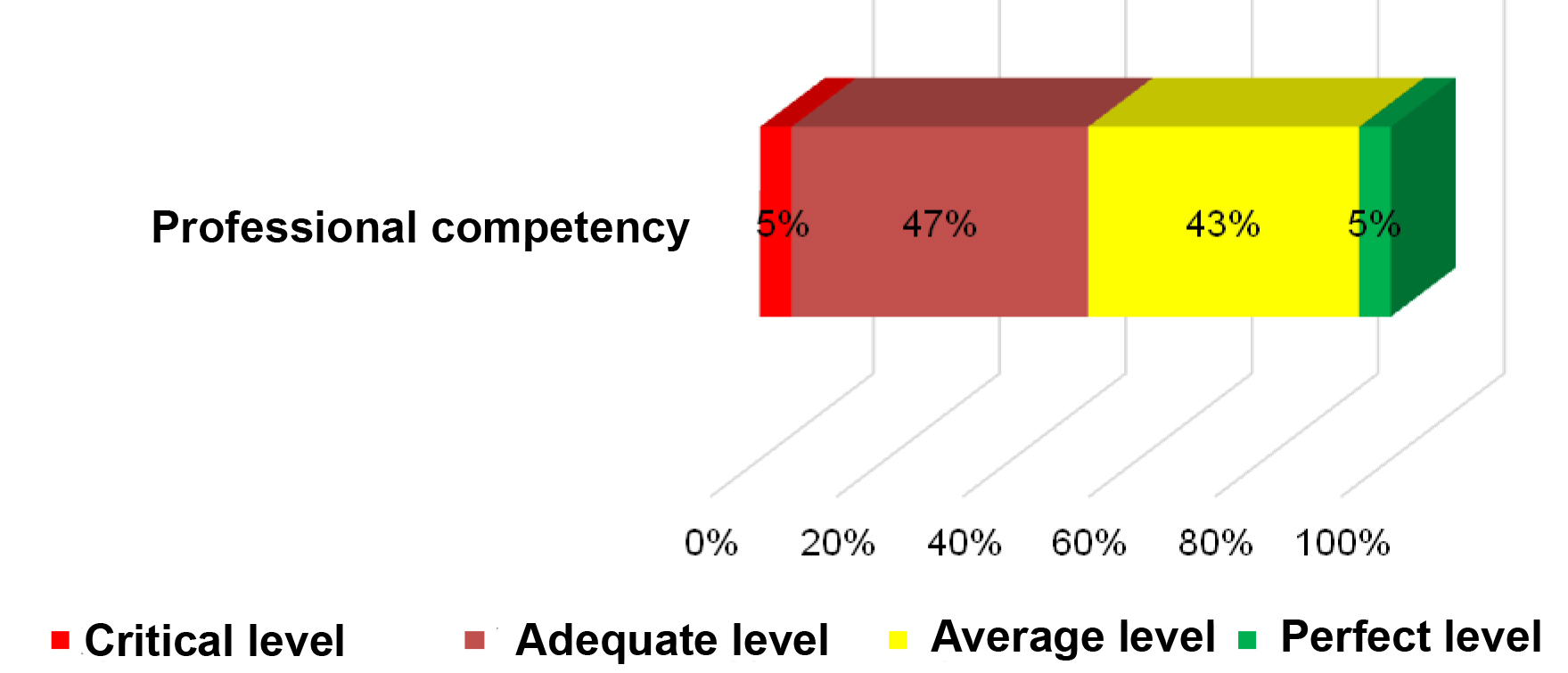
Figure 2. Rankings of professional competency
Conclusion. The academic physical education process must be designed with due emphasis on the quality of every relevant education component, with the quality being largely dependent on the competences and a variety of the relevant objective and subjective factors including: availability and condition of the informational basis, sport facilities, instruments, academic staff, legal and regulatory framework, finance, management, institutional capacity and operational components of the education system. A special role in this context is played by the modern innovative education and practical technologies for the personal physical culture building process, including the relevant focused, problem-solving, contextual, role playing, interactive education, transformation, competency-building and institutional capacity building initiatives (relevant centres, clubs, elective courses, advanced education courses, elective training models etc.), plus modern research projects.
References
- Vilenskiy M.Y., Gorshkov A.G. Fizicheskaya kultura i zdorovy obraz zhizni studenta. Ucheb. posobie [Physical Culture and Healthy Lifestyle of Student. Study guide]. 2nd ed., ster.. Moscow: KNORUS publ., 2012, 240 p.
- Gorbunov G.D., Gogunov E.N. Psikhologiya fizicheskoy kultury i sporta. Uchebnik dlya stud. vyssh.ucheb. zavedeniy [Psychology of physical culture and sports. Textbook for university students]. Moscow: Akademiya publ., 2009, 256 p.
- Kokoulina O.P. Osnovy teorii i metodiki fizicheskoy kultury i sporta. Ucheb. posobie [Fundamentals of theory and methods of physical culture and sports. Study guide], Moscow: PRUE publ., 2016, 113 p.
- Lubysheva L.I. Teoretiko-metodologicheskie i organizatsionnye osnovy formirovaniya fizicheskoy kultury studentov. Avtoref. dis. dokt. ped. nauk [Theoretical-methodological and organizational basics of development of students' physical culture. Doctoral diss. abstract (Hab.)]. Moscow: GTSOLIFK publ., 1992.
- Masalova O.Y. Formirovanie tsennostnogo otnosheniya studentov k zdorovyu i fizicheskoy kulture. Uchebno-metod. posobie [Cultivating students' value attitude to health and physical culture. Teaching aid]. Moscow, 2009, 202, P.76.
- Nikiforov G.S. Psikhologiya zdorovya. Uchebnik dlya vuzov [Psychology of health. University textbook]. St. Petersburg: Piter publ., 2006, 607 p.
- Petkov V.A. Formirovanie fizicheskoy kultury lichnosti v sisteme nepreryvnogo obrazovaniya: sostoyanie, problemy i perspektivy [Development of a personal physical culture in continuous education system: status, problems and prospects]. Moscow: MPSU publ., 1999, 267 p.
- Rasporyazhenie Pravitelstva RF ot 07.08.2009 no. 1101-r «Ob utverzhdenii Strategii razvitiya fizicheskoy kultury i sporta v Rossiyskoy Federatsii na period do 2020 goda» [RF Government Order dated 07.08.2009 no. 1101-r "On approval of the Strategy for Development of Physical Culture and Sports in the Russian Federation for the Period to 2020"]. Available at: http://www.consultant.ru/cons/cgi/online.cgi?req=doc&base=LAW&n=90500&fl... , free access. (Accessed: 15.01.2017)
- Solovyev G.M., Belova L.V. Podgotovka spetsialistov v oblasti fizicheskoy kultury k realizatsii zdorovyesberegayuschey pedagogicheskoy deyatelnosti [Physical education specialist training for health-protecting teaching activity]. Moscow: Ilexa publ., 2011, 180 p.
- Solovyev G.M., Tarasenko I.R. Formirovanie sotsialno-dukhovnykh tsennostey zdorovyesberegayuschey zhiznedeyatelnosti studencheskoy molodezhi sredstvami fizicheskoy kultury [Cultivating students' social and spiritual values of healthy living using physical education]. Moscow: Ilexa publ., 2010, 194 p.
- Federalny zakon ot 29.12.2012 no. 273-FZ (red. ot 03.07.2016, s izm. ot 19.12.2016) «Ob obrazovanii v Rossiyskoy Federatsii» (s izm. i dop., vstup. v silu s 01.01.2017) [Federal Law dated December 29, 2012 no. 273-FL (as amended on 03.07.2016, as amended on 19.12.2016) "On Education in the Russian Federation" (with amendments and additions, effective from 01.01.2017)].
Corresponding author: Kokoulina.OP@rea.ru
Abstract
The study was designed to explore the current motivations of the Moscow university students for the academic physical education curricula that may be cultivated by educators. It outlines the key teacher’s competences required to effectively motivate students for physical education; and lists requirements to the education system quality in this domain.
The authors conclude that success of the academic physical education process largely depends on the physical education teachers and their competences. The academic physical education process must be designed with due emphasis on the quality of every relevant education component, with the quality being largely dependent on the competences and a variety of the relevant objective and subjective factors including: availability and condition of the informational basis, sport facilities, instruments, academic staff, legal and regulatory framework, finance, management, institutional capacity and operational components of the education system. A special role in this context is played by the modern innovative education and practical technologies for the personal physical culture building process, including the relevant focused, problem-solving, contextual, role playing, interactive education, transformation, competency-building and institutional capacity building initiatives (relevant centres, clubs, elective courses, advanced education courses, elective training models etc.), plus modern research projects.




 Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE
Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE