Analysis of the implementation of projects for the development of sports infrastructure in the Russian Federation
Фотографии:
ˑ:
D.G. Stepyko1
D.S. Aleksandrov1
D.V. Gracheva1
Javid Allahverdi Ogly Farzaliev1
1Plekhanov Russian University of Economics, Moscow
Keywords: sports infrastructure, public-private partnership, sports facilities, financing mechanisms, physical culture and sports.
Background. The list of the key priorities of the social and economic development policies of the Russian Federation for the period up to 2020 provides, among other points, new social development mechanism building initiatives including healthy lifestyle promotion ones. Efforts to establish facilitating conditions for the people to accept healthy lifestyle including habitual physical culture and sports; develop accessible sport infrastructure; and step up the Russian sports competitiveness on the global arenas – were mentioned among the key strategic goals of the governmental policies in the national physical culture and sports sector.
Objective of the study was to analyse the sport infrastructure development process in the Russian Federation with an emphasis on progress of the most efficient public-private partnership (PPP) projects and relevant operational arrangements.
Study results and discussion
Analysis of the best international and national experiences
Generally, the best international practical experience of projects in the physical culture and sports sector demonstrates their high potential benefits for investments as the profitability rates may come to as much as 34% with the payback periods normally varying at 7-10 years. Commercial benefits of such projects are normally increased by the large-scale sport facilities being designed to provide not only purely competitive but also entertainment and trade services; and by small sporting institutions being integrated into a network managed by a single operator. Some internationally popular project models have paved their way to the Russian market – particularly the integrated sport infrastructure development project model. Generally the following success criteria of the physical culture and sport sector projects are typical for the modern Russian practices: sport facilities specialising in a single discipline (tennis, football etc.) tend to be less profitable than the universal ones – that offer a wide variety of sport services; presently the sport infrastructure development businesses largely prefer compact multifunctional universal sport project design with a range of gyms and transformable stadiums customisable for any event and season; and it is fitness centres, swimming pools, aquatic parks and health rehabilitation service centres that are considered the most profitable elements of such integrated infrastructural projects.
PPP project implementation specifics in the national physical culture and sports sector
The growing need for the sport infrastructure development and rehabilitation projects including those in the public physical culture and sports sector on the one hand, and the existing budgetary constraints on the other hand – explain why the increasing priority is given today to the PPP instruments in particular and initiatives to lure private investments to the sector projects on the whole. The PPP mechanism may be described as the way to lure private investments for socially important purposes. The existing national legislation presently makes provisions for the following two PPP models: concession PPP contracts and other PPP contracts.
As things now stand in the national physical culture and sports sector, at different progress stages are 23 projects of 873 PPP projects in total – versus 12 PPP projects in 2014.
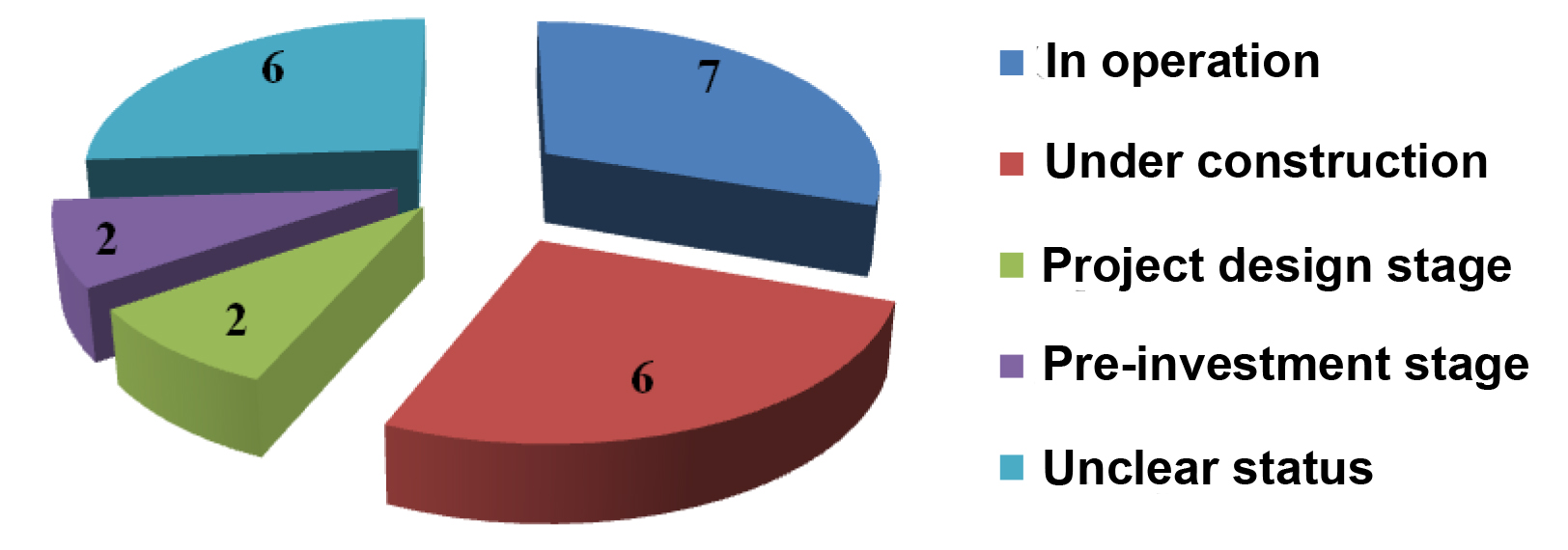
Figure 1. PPP projects in the national physical culture and sports sector classified by the progress stages, numbers
The PPP projects in the national physical culture and sports sector that are under implementation or nearing implementation are dominated by the regional ones, and this fact may be indicative of the presently higher demand for the physical culture and sports development services at the local level and, possibly, of a higher commitment of the local governments for co-financing of such projects.
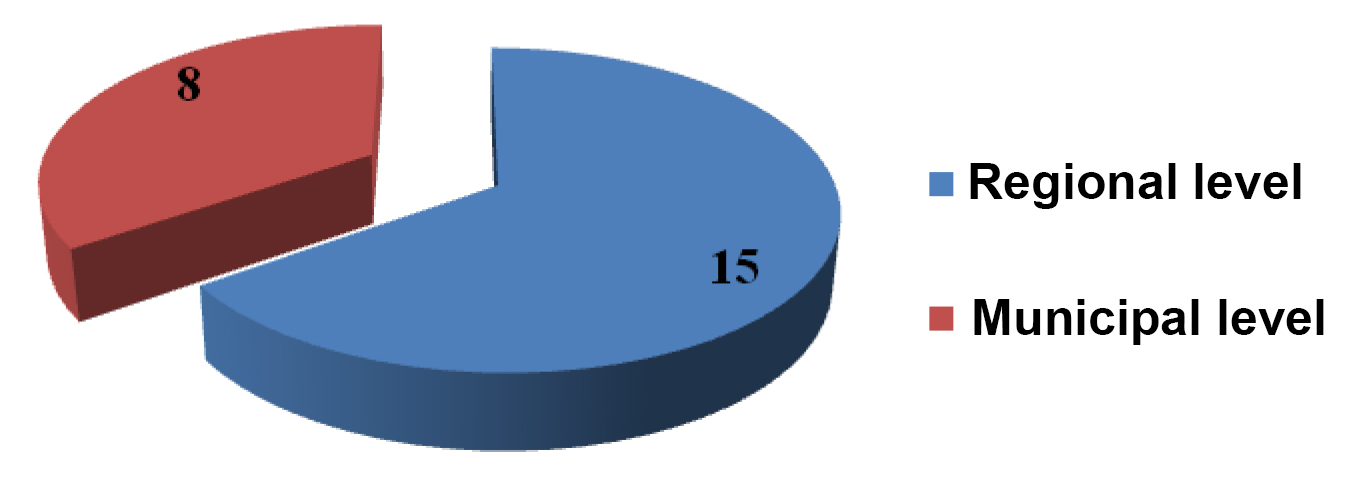
Figure 2. PPP projects in the national physical culture and sports sector classified by levels, numbers
Sport-discipline-specific analysis of the current PPP projects at different progress stages in the national physical culture and sports sector shows that most popular at this juncture are the PPP projects in the following sport disciplines: a range of ice sports; water sports; football and other team sports.
The study data demonstrated the share of physical culture and sports projects in the total project activity being still insignificant albeit the social importance of the physical culture and sports projects puts them on top of the list of priorities of the social infrastructure development initiatives. However, the private investment in these projects is now largely hampered by the following factors: lack of consistent standards for the sport infrastructure projects and, hence, a widely varied cost of square meter across the country; lack of project standards that make them replicable, with the poor standardisation making it difficult for a potential private investor to estimate the costs and benefits of a construction project; still inconsistent government regulations and provisions for the PPP projects in different regions; the still high mistrust of the potential investors to the “topical” PPP instruments further aggravated by too high banking service risks for the PPP projects under the existing project financing provisions.
It should be mentioned that PPP projects in the national sport sector bring many benefits for the national economy including: savings in the budgetary assignments to the relevant Federal and local physical culture and sport initiatives; boost for the entrepreneurial activity in the socially important sector, with the relevant health and employment (new jobs) benefits for the local communities; and growth of tax revenues in the local and national government budgets from the growing sport sector.
The above benefits of the PPP projects in the national physical culture and sports sector cannot be attained if the ambitious projects to develop new sport stadiums, sport grounds and health facilities and restore or rebuild the existing ones are still underfinanced by the national budget. In such a situation the national government has to vest the local governments with due responsibilities and decision-making freedom in the matters related to the PPP projects and their contracting activity.
Conclusion. In view of the proven benefits of the public-private partnerships in the national physical culture and sports sector, it would be beneficial for the government to set and pursue systemic policies to lure private capitals to the sector.
First, the regional legislative and regulatory framework needs to be updated to offer, among other things, tax benefits to the companies undertaking projects in the national physical culture and sports sector.
Second, the relevant accessible lending mechanisms need to be put in place with due debt service and interest coverage mechanisms for bank loans, plus guaranties for loan agreements from the local governments.
Third, a clear public-private interaction algorithm must be offered to the potential investors to encourage their cooperation with the local governments, with the due balance of project risks, transparent bidding and contracting procedures and/or joint PP project design teams formed to consider and facilitate the private concession initiatives.
The study found that neither of the above initiatives may be successful enough unless supported by the budgetary financing and investor’s commitment for the project implementation without due financial and economic efficiency substantiating data.
References
- Varnavskiy V.G., Klimenko A.V., Korolev V.A. Gosudarstvenno-chastnoe partnerstvo. Teoriya i praktika. Ucheb. posobie [Public private partnership. Theory and practice. Study guide]. Moscow: State university - Higher School of Economics publ., 2010, 287 p.
- Mataev T.M. Riski v sfere gosudarstvenno-chastnogo partnerstva [Risks in public-private partnership sphere]. Problemy sovremennoy ekonomiki, 2014, no. 2 (50), pp. 180-185.
- O gosudarstvenno-chastnom partnerstve, munitsipalno-chastnom partnerstve v Rossiyskoy Federatsii i vnesenii izmeneniy v otdelnye zakonodatelnye akty Rossiyskoy Federatsii: federalny zakon RF ot 01.07.2015 # 224-FZ [On public-private partnership, municipal-private partnership in the Russian Federation and amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation: Federal Law of the RF No. 224-FZ dated 01.07.2015]. Rossiyskaya gazeta, 2015, no. 6727.
- O kontsessionnykh soglasheniyakh: federalny zakon RF ot 21.07.2005 # 115-FZ [On concession agreements: Federal Law of the RF dated July 21, 2005 No. 115-FL]. Rossiyskaya gazeta, 2005, no. 3830.
- Petrikova E.M., Slobodyanyuk N.V. Gosudarstvenno-chastnoe partnerstvo v sportivnoy industrii Rossii [Public-private partnership in Russian sports industry]. Problemy ekonomiki, 2013, no. 3, pp. 111-119.
- Rasporyazhenie Pravitelstva RF ot 17.11.2008 # 1662-r «O Kontseptsii dolgosrochnogo sotsialno-ekonomicheskogo razvitiya Rossiyskoy Federatsii na period do 2020 goda» (vmeste s «Kontseptsiey dolgosrochnogo sotsialno-ekonomicheskogo razvitiya Rossiyskoy Federatsii na period do 2020 goda») [RF Government Decree 17.11.2008 No. 1662-r "On the Concept of Long-Term Socioeconomic Development of the Russian Federation for the Period till 2020" (in addition to the "Concept of Long-Term Socioeconomic Development of the Russian Federation for the Period till 2020").].
- Rasporyazhenie Pravitelstva RF ot 07.08.2009 # 1101-r «Ob utverzhdenii Strategii razvitiya fizicheskoy kulturyi i sporta v Rossiyskoy Federatsii na period do 2020 goda [RF Government Order dated 07.08.2009 № 1101-r "On approval of Physical Culture and Sports Development Strategy in the Russian Federation for the Period till 2020].
Corresponding author: stepunit@mail.ru
Abstract
Subject to the study were some aspects of the sport infrastructure development in the Russian Federation with an emphasis on the most efficient public-private partnership (PPP) projects implementation and relevant operational arrangements at different levels.
In view of the proven benefits of the PPP projects in the national physical culture and sports sector, the authors offer a range of potential initiatives to: lure private investments in the sector; develop the regional regulatory framework to offer tax benefits to the national physical culture and sports sector operators; secure more accessible loan financing mechanisms; and develop a PPP algorithm for the investors’ cooperation with the regional governments put on a fair basis.
The study found that neither of the above initiatives may be successful enough unless supported by the budgetary financing and due commitment of the investor for the project implementation without due financial and economic efficiency substantiating data.
The authors came to conclusion that the PPP may be beneficial for implementation of socially important projects by the government and for the private investors who are offered new beneficial projects for investments creating new jobs; and offered a set of potential initiatives to activate the PPP in the present situation.




 Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE
Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE