"Children of Asia" International sports games: growth process
Фотографии:
ˑ:
V.V. Yadreev1
A.V. Filippov1
E.P. Kudrin1
S.P. Skryabin1
1Institute of Physical Culture and Sports of Ammosov North-Eastern Federal University, Yakutsk
Keywords: Children of Asia International Sports Games, Olympic Games, junior athletes.
Background. The motto “Olympic year not only for Olympians” has long been popular in Yakutia – and one of the Olympic spirit manifestations is the Children of Asia International Sports Games that have been held in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) once in four years since 1996 timed to the summer Olympic Games.
The Children of Asia International Sports Games are generally much similar to Youth Olympics, sport festivals and “senior” Olympic Games differing only in the scale of the event. The Children of Asia ISG involve multiple modern sport facilities, an Olympic Village, special information and transport network, a security system, and the participants may enjoy a multisided and interesting cultural program.
The Children of Asia International Sports Games are driven by the idea that junior Asian athletes should have their own top sporting event similar to those that take place on the other continents. In this context, the present study was designed to analyse the progress the Children of Asia International Sports Games have made for their history, with the following goals:
1. Identify the inspiration factors for the Children of Asia International Sports Games.
2. Make a progress analysis of the Children of Asia International Sports Games.
Study results and discussion. The Children of Asia International Sports Games were basically inspired by the fast growth of the popular mass sports including the children’s and youth sports the world over. It was the European Youth Olympic Festivals (EYOF) initiated in 1991 by Jacques Rogge (chairman of the Association of European Olympic Committees at that time) that may be considered the first multi-sport event for junior athletes. The first 1991 EYOF in Brussels brought together 2048 athletes and 33 official national Olympic committees; and by the year of 1995 the number of national Olympic Committees grew to 47 and stayed at this level since then. Prior to 1995 the participation had not that high, but since 1997 the Festivals attracted around 2500 athletes each time.
As for the Children of Asia International Sports Games, they have been widely recognised for a relatively short time largely due to their great sport accomplishments and the class of the competitors many of whom are highly reputed on the global sport arenas. The positive global response to the idea of the Children of Asia International Sports Games and their growing popularity is confirmed by the letter from Juan Antonio Samaranch, IOC President since 1980, who welcomed the participants to the event from the Olympic Congress in Moscow and awarded Mikhail Nikolayev, President of the Sakha Republic, with a memorial Olympic medal.
The I Children of Asia International Sports Games brought together 250 junior athletes from Kazakhstan, China, Korean Republic, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Thailand, Agin-Buryat Autonomous Area, Buryatia, Tyva and Yakutia who competed for 224 medals: see Figure 1.
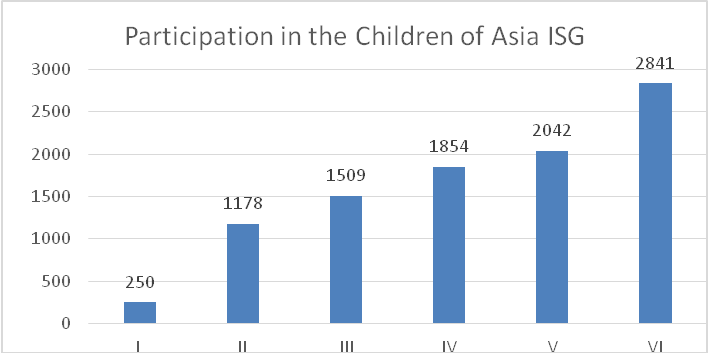
Figure 1. Children of Asia International Sports Games: participation statistics
The II “Children of Asia International Sports Games (August 4-13, 2000) were held in Yakutsk and brought together 1178 junior athletes from 23 Russian regions and 13 world nations including Bangladesh, Vietnam, India, Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Malaysia, Mongolia, Korean Republic, Singapore, Taiwan, Philippines and Japan. The athletes competed for 129 medal sets in 16 sport disciplines including basketball, boxing, ethnic Hapsagay wrestling, volleyball, freestyle wrestling, judo, track and field sports, mas-wrestling (ethnic stick pulling sport), international draughts, table tennis, Nordic combined events, artistic gymnastics, dance sport, archery, rhythmic gymnastics, chess and Yakut ethnic jumping sport: see Figure 2.
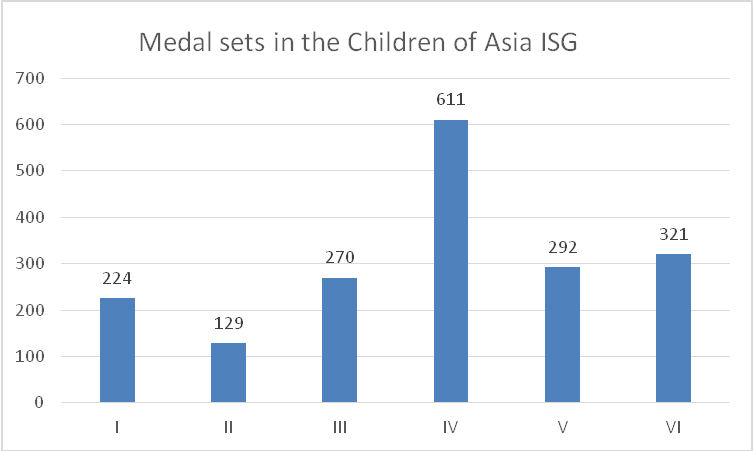
Figure 2. Children of Asia International Sports Games: medal sets
The III Children of Asia International Sports Games were held on July 23-30, 2004 in Yakutsk and brought together 1509 junior athletes of 11 nations including Armenia, Vietnam, India, Kazakhstan, China, Korean Republic, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Thailand, Turkey and 26 Russian regions. The athletes competed for 270 medal sets in 17 sport disciplines including basketball, boxing, volleyball, freestyle wrestling, judo, track and field sports, mas-wrestling (ethnic stick pulling sport), international draughts, table tennis, powerlifting, artistic gymnastics, chess and Yakut ethnic jumping sport: see Figure 3.
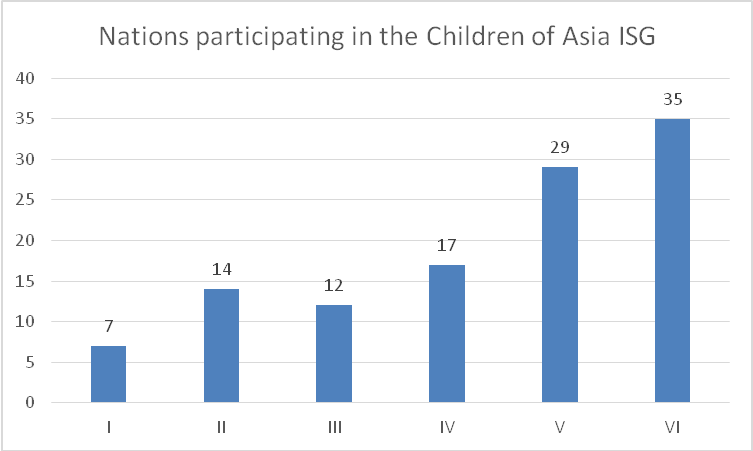
Figure 3. Nations participating in the Children of Asia International Sports Games
It may be worth mentioning that the II, III and IV Children of Asia International Sports Games were held under the auspices of the International Olympic Committee (IOC). The IV “Children of Asia International Sports Games were held on July 3-13, 2008 in 18 sport disciplines in three cities of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia).
The V Children of Asia International Sports Games were held on the Russian Presidential Decree on July 4-16, 2012; and the athletes competed in 20 sport disciplines including (for the first time) swimming, sambo and freestyle wrestling for hearing-impaired children. This time the Children of Asia International Sports Games were held under the auspices of the IOC and UNESCO: see Figure 4.
The VI Children of Asia International Sports Games brought together 2841 junior athletes from 38 countries including Azerbaijan, Bangladesh, Bahrain, Bhutan, Vietnam, Hong Kong, Irak, Iran, Yemen, Kazakhstan, Cambodia, China, Korean Republic, Kuwait, Laos, Maldives, Mongolia, Nepal, Pakistan and some others.
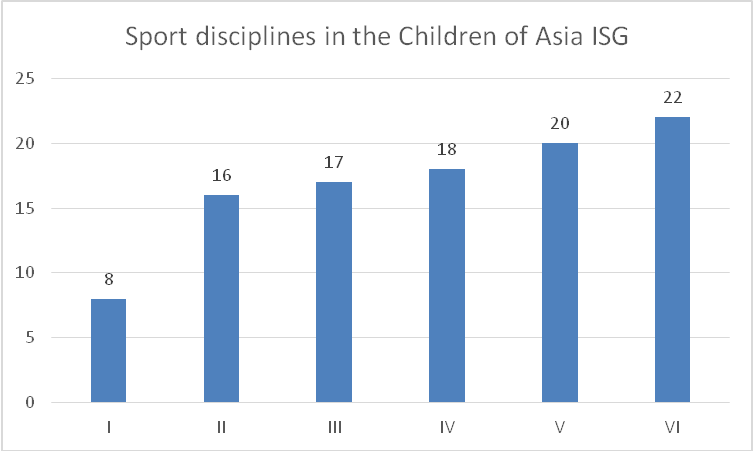
Figure 4. Sport disciplines in the Children of Asia International Sports Games
Conclusion. The first Children of Asia International Sports Games brought together only 250 athletes from seven countries who competed for medals in only eight sport disciplines as compared to the VI Children of Asia International Sports Games that involved more than two thousand athletes from 35 nations who competed for 321 medal sets in 22 sport disciplines; and these statistics shows the progress made by the event for this period. For the last 20 years the Children of Asia International Sports Games have made a great progress and won a great popularity the world over – largely due to the efforts of many enthusiasts who competed and otherwise contributed to the progress of the Games. Presently the Children of Asia International Sports Games enjoy a special status and are held under the auspices of the International Olympic Committee.
In the context of the progress data presented herein, the Children of Asia International Sports Games may be viewed as a logical product of the modern international youth sporting movement that not only generates great sport achievements but also facilitates exchange of the cultural and traditional values of the participating nations and helps the new generations accept the traditional values and philosophy of the Olympic movement.
References
- Steinbach V.L. Bolshaya olimpiyskaya entsiklopediya. V 2 t. [Big Olympic Encyclopedia. In 2 volumes]. Moscow: Olimpia press publ., 2006.
- Miller D., Ofitsialnaya istoriya Olimpiyskikh igr [Official History of the Olympic Games]. 2003, 550 p.
- Peshkov A. «Deti Azii» – lokomotiv Yakutii [o 15-letii so dnya starta nachala igr «Deti Azii] [Children of Asia - the driving force of Yakutia [on the 15th anniversary of Children of Asia Games]. Yakutia, 2011. Aug., 10, p. 1.
- Yakovlev G. Prezentatsiya na Aziade [o prezentatsii MSI «Deti Azii-2012» v stolitse Kazahstana gorode Astane] Presentation at Asian Games [on presentation of Children of Asia-2012 ISG in the capital of Kazakhstan, Astana city]. Yakutia, 2011. Feb., 2, p. 1.
Corresponding author: fizkult@teoriya.ru
Abstract
The Children of Asia International Sports Games were designed to give a field for junior athletes of Asia to meet and compete on sport grounds, contribute to the global friendship and cultivate due respect and tolerance to the opponents. The Children of Asia International Sports Games are governed by the Olympic tenets to create a better world via friendship, solidarity and fair play spirit cultivated in the young competitors and their fans.
The article gives a progress analysis of the Children of Asia International Sports Games records for the period of 1996 to 2016. The analysis of the Games records and accomplishments showed progress of the popular international competitive formats for young people that not only generate great sport achievements but also facilitate exchange of the cultural and traditional values of the participating nations and help the new generations accept the traditional values and philosophy of the Olympic movement.




 Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE
Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE