Athletic training process improvement at planning stage (case study of Tyumen sport schools)
Фотографии:
ˑ:
Theory and Practice of Physical Culture № 12 2016
M.V. Alekseeva1
N.B. Soloshenko1
A.V. Kolychev1
Associate Professor, PhD D.N. Makaridin2
Department of Sport and Youth Policy of the Tyumen city Administration
Tyumen State University, Tyumen
Keywords: monitoring, management decisions, staged medical examinations, management function, training process.
Background. The city of Tyumen is presently a ground for implementation of a systemic innovation strategy project in the municipal physical culture and sports sector [2, 3, 5]. One of the missions of the strategy is to improve the education and training process quality at local sport schools and verify it by the junior athletes’ health and physical fitness progress monitoring to advance the education and training planning component.
It is a matter of common knowledge that a planning process takes into account the athlete’s fatigue and post-training recovery regularities. The main goal of the planning process is to identify, with due account of every factor of influence, the key performance criteria for the athlete’s performance modelling for the period covered by the planning. [1]. Subject to the planning process are the training process content, means and forms. It is also pivotal that the planning process is based on due understanding of the current mental, physical and functional statuses of the athlete.
Objective of the study was to use the Tyumen athletes’ physical health and physical fitness progress monitoring data analysis to identify and substantiate the most efficient planning methods for the education and training process.
Study results and discussion. It was in the period of 2013 through 2014 that special initiatives to monitor, analyze, assess and forecast the athletes’ health and physical fitness progress at advanced education establishments were taken within the frame of the Sport School Pupils’ Health and Physical Fitness Monitoring Project implementation process [4]. As seen from the findings of the study, 83% of the athletes had the general physical fitness and physical development rates being equal or above the average levels, and only 17% of the athletes from the advanced education establishment were tested with below-average rates. At the same time, analysis of the athletes’ physical performance test data showed the general endurance and muscular strength rates being insufficient, and this deficiency was found to directly influence the athlete’s physical workability rates.
The test data obtained by the progress monitoring project included the low vital capacity and strength rates (see Figures 1, 2), with 51% of the young men and 33% of the young women tested with low vital capacity rates. Furthermore, 48% of the young men and 62% of the young women were tested with low strength rates.
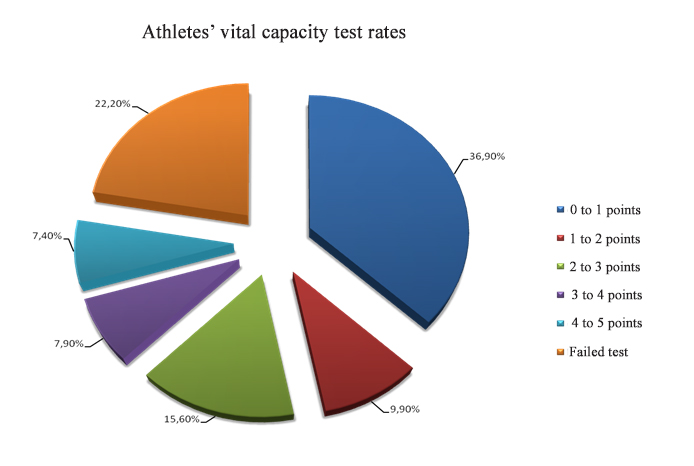
Figure 1. Athletes’ vital capacity test rates
Given hereunder on Figure 2 are the strength rates of the 5864 young men and 4624 young women tested under the study.
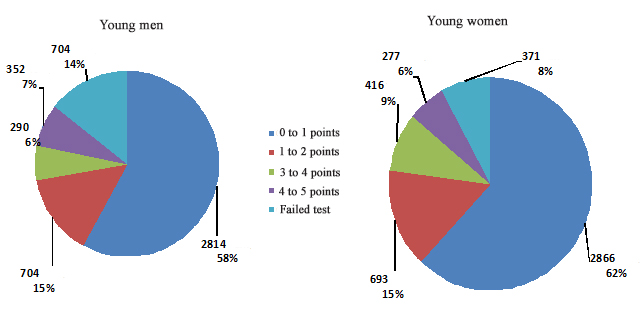
Figure 2. Athletes’ strength test rates
Special physical fitness rates of the young men and women were estimated under the study with classification by the age groups and sport disciplines known to be of the highest positive effect on special physical abilities, including basketball, boxing, artistic gymnastics, Greco-Roman wrestling, judo, ski racing, swimming, climbing, sport dances, tennis, figure skating, football, ice hockey and rhythmic gymnastics.
Leading in the physical performance tests in every age group were the athletes representing the following sport disciplines: artistic gymnastics, judo and climbing. Tested with below-average physical performance rates were ice hockey and football players. Generally, the monitoring project data showed that coaches should make more emphasis on the general endurance and muscular strength development practices.
Furthermore, our analysis of the staged medical examination data obtained by the Tyumen-based Neptun Health Centre (headed by Professor, Head Physician, Doctor of Medicine S.B. Tsiryatyeva) showed that the athletes’ cardiovascular system responses to sub-maximal workloads were dominated by hypokinetic-type reactions (see Figure 3).
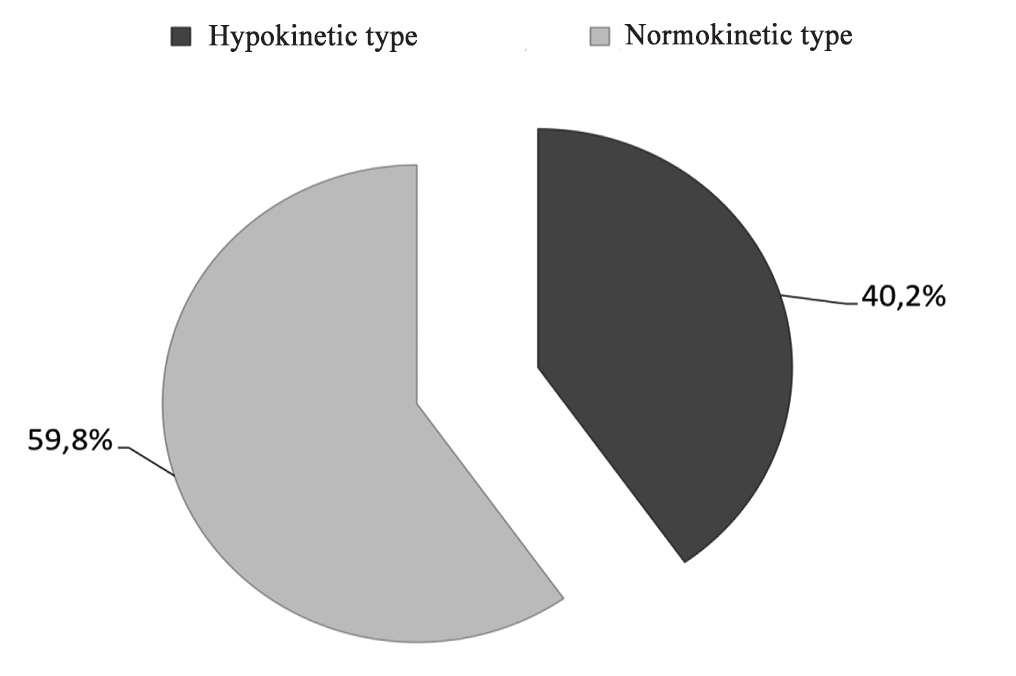
Figure 3. Athletes’ cardiovascular system responses to sub-maximal workloads
Blood composition analysis diagnosed 78% of the athletes with respiratory alcalosis; 97.3% with serotonin and dopamine imbalance; 98% with imbalance of sex hormones; and 74% with insulin imbalance. These imbalances may be of negative effect on the satisfaction with accomplishments and contribute to the chronic fatigue (see Figure 4).

Figure 4. Correlation of blood composition with fatigue rates and professional satisfaction rates
It is the staff members having the relevant special background that are in charge of professional planning process in the sector. However, there is still the question of whether or not such a background guaranties the due ability to design optimal plans to meet the modern requirements, duly prioritize the process objectives and select the most efficient solutions. Regretfully, the existing traditional planning methods and their practical outcomes are commonly recognized not efficient enough.
Studies of the planning documentation quality, relevance and compliance to the modern requirements in the context of the coaches’ special background quality showed that even а formal special background cannot guarantee the planning process quality. It may be due to the fact that the planning responsibility prior to the above project has never been ranked among the top priorities and, hence, the planners lacked practical experience in planning documentation. As a result of the monitoring project, the relevant management decisions were made to improve the education and training process efficiency at municipal sport schools. In addition, practical recommendations were made to help adjust the design and content of the training process planning component (see Figure 5).
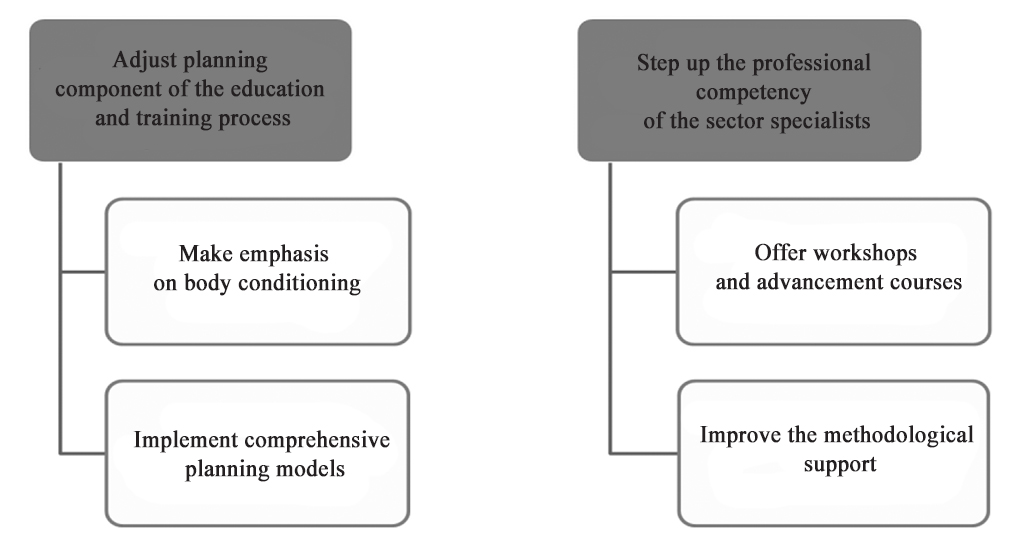
Figure 5. Management decisions and their components designed to improve the training process quality
Within the frame of the education and training process planning component improvement project, we developed the annual athletic training process cycling system (including macro-cycle, meso-cycle and micro-cycle) for every sport discipline and stage of the training process (the system includes 720 subsystems). Presently the Department exercises a strict control of the planning documentation development process with an emphasis on its content and practical implementation in the educational process (see Figure 6).
Special skills advancement courses, methodological and practical workshops, open-doors sessions and master classes are offered to advance the skills of the staff members of the municipal physical culture and sports sector. A special priority is also given to the efforts to develop the sport reserves. As things now stand, trained by the special sport classes (and sport-centred education classes) are 2074 people majoring in 16 sport disciplines; and Sport Schools #68 and #22 offer special pre-professional training in Physical Education, with the school graduates being given the opportunity to continue education at special education establishments followed by practical employment in the sector.

Figure 6. Children’s and youth sports management quality control system
We have attained – through the relevant above-described planned initiatives and the second-stage process monitoring initiative and data analyses – certain progress as verified by the growing numbers of the skilled athletes and winners of the regional sports events. Given on Figures 7, 8 and 9 hereunder are the municipal sports progress data with the relevant growth rates. It should be noted that these activities have been designed on an uninterrupted basis and subject to permanent management and control by the Sports and Youth Policy Department of the Tyumen Municipality in cooperation with Physical Culture Institute of Tyumen State University.
Figure 7. Growth of sport categories
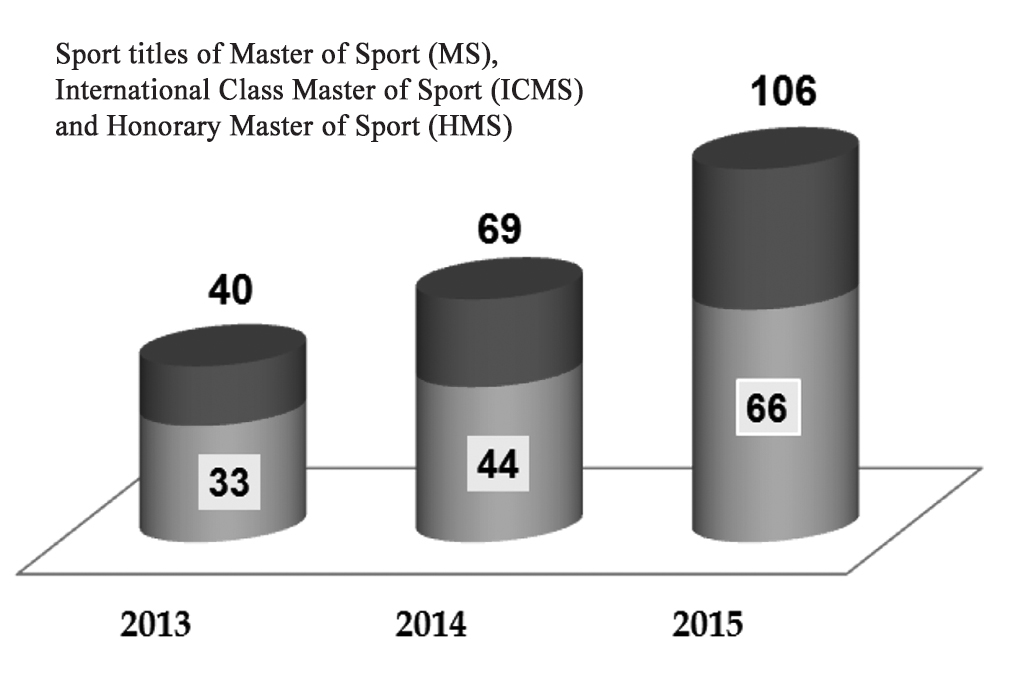
Figure 8. Growth of sport titles
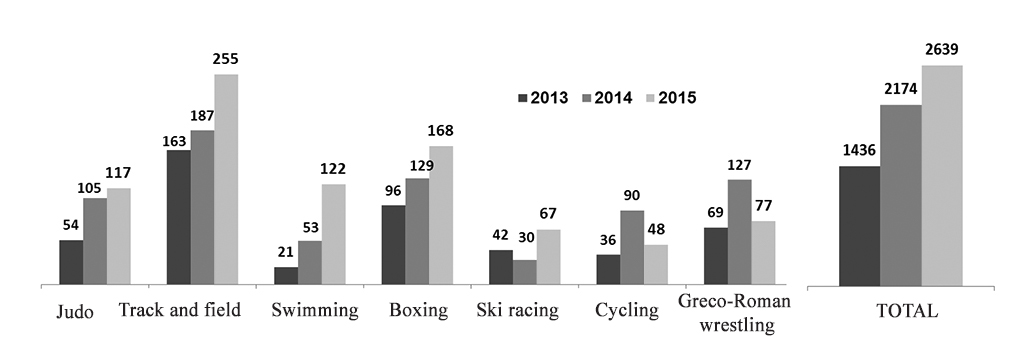
Figure 9. Numbers of winners and runner-ups of regional competitions
Conclusion. The study data and analyses helped find the reasons for the insufficient physical development and progress of Tyumen athletes. We believe the deficiencies are largely due to the poor abilities of the coach-instructors to design and plan the training process as required by the modern theory, practice and the valid regulatory requirements to the CYSS education process.
The study also profiled the recent progress in the sport-school education and training process planning. The situation was found to be improving due to the target initiatives by the Sports and Youth Policy Department of the Tyumen Municipality (including skills advancement courses, focus meetings, explanatory discussions, workshops for some categories of coaches etc.). At this stage of the initiatives, the planning documents have been virtually cleared of serious methodological errors, the success being partially due to the enthusiastic and conscious contributions from the coaches striving to master the modern planning process.
References
- Bal'sevich V.K. Sportivno orientirovannoe fizicheskoe vospitanie: obrazovatel'ny i sotsial'ny aspekty, teoriya i praktika fizicheskoy kul'tury (Sports-centered physical education: educational and social aspects of theory and practice of physical culture) / V.K. Bal'sevich. – 2003. # – 5. – P. 19-22.
- Golichenko O.G. Natsional'naya innovatsionnaya sistema Rossii: sostoyanie i puti razvitiya (National innovation system of Russia: state and development trends) / O.G. Golichenko. – Moscow: Nauka, 2006. – P. 396.
- Korotkova E.A. Upravlenie innovatsiyami v obrazovanii (Innovation management in education) / E.A. Korotkova // Fizicheskaya kultura: vospitanie, obrazovanie, trenirovka. – 2010. – # 1. – P. 2-4.
- Korotkova E.A. Organizatsiya monitoringa fizicheskogo zdorov'ya i fizicheskoy podgotovlennosti yunykh sportsmenov g. Tyumeni (Physical health and fitness monitoring procedure in application to junior athletes in Tyumen) / E.A. Korotkova, N.B. Soloshenko, M.V. Alekseeva, M.A. Naumova // Teoriya i praktika fiz. kultury. – 2013. – # 12. – P. 21-24.
- Khromin E.V. O strategii sistemnykh innovatsiy v formirovanii fizicheskogo zdorov'ya podrastayushchego pokoleniya (Systemic innovation strategies in promotion of physical health of younger generation) / E.V. Khromin, E.A. Korotkova, A.E. Stepanov // Fizicheskaya kultura: vospitanie, obrazovanie, trenirovka. – 2013. – № 4. – P. 2-5.
Corresponding author: kolychevav@tyumen-city.ru
Abstract
A planning process as a natural part of any social activity may be also viewed as a key component of a management process. Planning is ranked among the most challenging process components in many professional fields, and the teacher’s profession is no exclusion. The article considers the issues of the athletic training process planning component quality improvement viewed as an important tool to excel the education and training process on the whole. The article reports data and analyses of the Tyumen athletes’ physical health and fitness monitoring project; staged medical examination process results; and the education and training process planning progress at municipal sport schools. Ways to improve the education and training process based on the study findings are proposed and discussed. As a result of the efforts taken by the Sports and Youth Policy Department of the Tyumen Municipal Government (including skills-advancement courses, focused meetings, explanatory discussions and workshops for different categories of coaches), the situation on the whole has been improved.




 Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE
Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE