General cultural competence building at sport and health tourism sessions
Фотографии:
ˑ:
Yu.A. Karvunis1
Dr.Med., Professor L.V. Kapilevich1, 2
1National Research Tomsk State University, Tomsk
2National Research Tomsk Polytechnic University, Tomsk
Keywords: sport and health tourism, competences, recreation.
Introduction. In recent years there has been a number of important changes in the organization of various forms of recreation of young people. Active trips are becoming the main form of recreation and the importance of sport and health tourism increases [5, 6]. Regional domestic tourism becomes an alternative to expensive foreign travel especially for young people [2, 3].
Sport and health tourism contributes to harmonious development of a person, overall strengthening of his/her body and cultivation of important social characteristics such as patriotism, respect for nature and knowledge of home region history [7, 8]. Sport and health tourism, as a socially significant phenomenon is included in the standards of All-Russian physical culture and sport complex "Ready for Labor and Defence" (GTO). Despite the fact that modern requirements for sport tourism differ from the standards adopted in 1972, the achievements of that period are the basis of methodological support of the preparation of tourists [1]. Therefore, it is very important to actualize the methodological support of sport and health tourism with the use of the competency building approach and search for new ways to attract young people to active forms of recreation [4].
Objective of the study was to analyze the formation of competence-based characteristics of students during sport and health tourism sessions.
Methods and structure of the study. Subject to experiment were male and female students of various Bachelor's degree programs from 4 universities of the city of Tomsk. The testing took place during the fall semester of the 2015-2016 academic year. 80 people were surveyed, 40 of them were actively engaged in sport and health tourism in the youth sections and clubs (20 male and 20 female students). The reference group also consisted of 40 students (20 males and 20 females). The testing of knowledge and skills included 5 blocks of questions. The selected competences were not directly related to the basic educational program of the Bachelor's degree program, instead, they represented an additional range of knowledge and skills in the field of sport and health tourism.
The first block – "Tourism Techniques" – included practical tasks and theoretical questions on basic tourism skills: how to tie knots, to set up a tent, to pack a backpack, to make a fire, the orienteering skills and skills for overcoming obstacles and etc.
The second block – "Regional Studies" – consisted of the questions on the characteristics of sports and health tourism and main recreational facilities of the Tomsk region.
The third block – "Ecology". An important component of youth tourism is cultivating careful attitude to recreational resources. This block contained questions on the ways of preserving nature and minimizing the human influence on the environment during trips.
The fourth block – "Security". The testing of the knowledge of major hazards for a tourist in our region and the skills necessary to ensure safety during travel such as first aid skills and knowledge of other survival techniques for emergency situations.
The fifth block – "Physical Training" – included the general physical fitness testing with the elements of sport and health tourism.
Results and discussion. The results are shown in Figure 1.
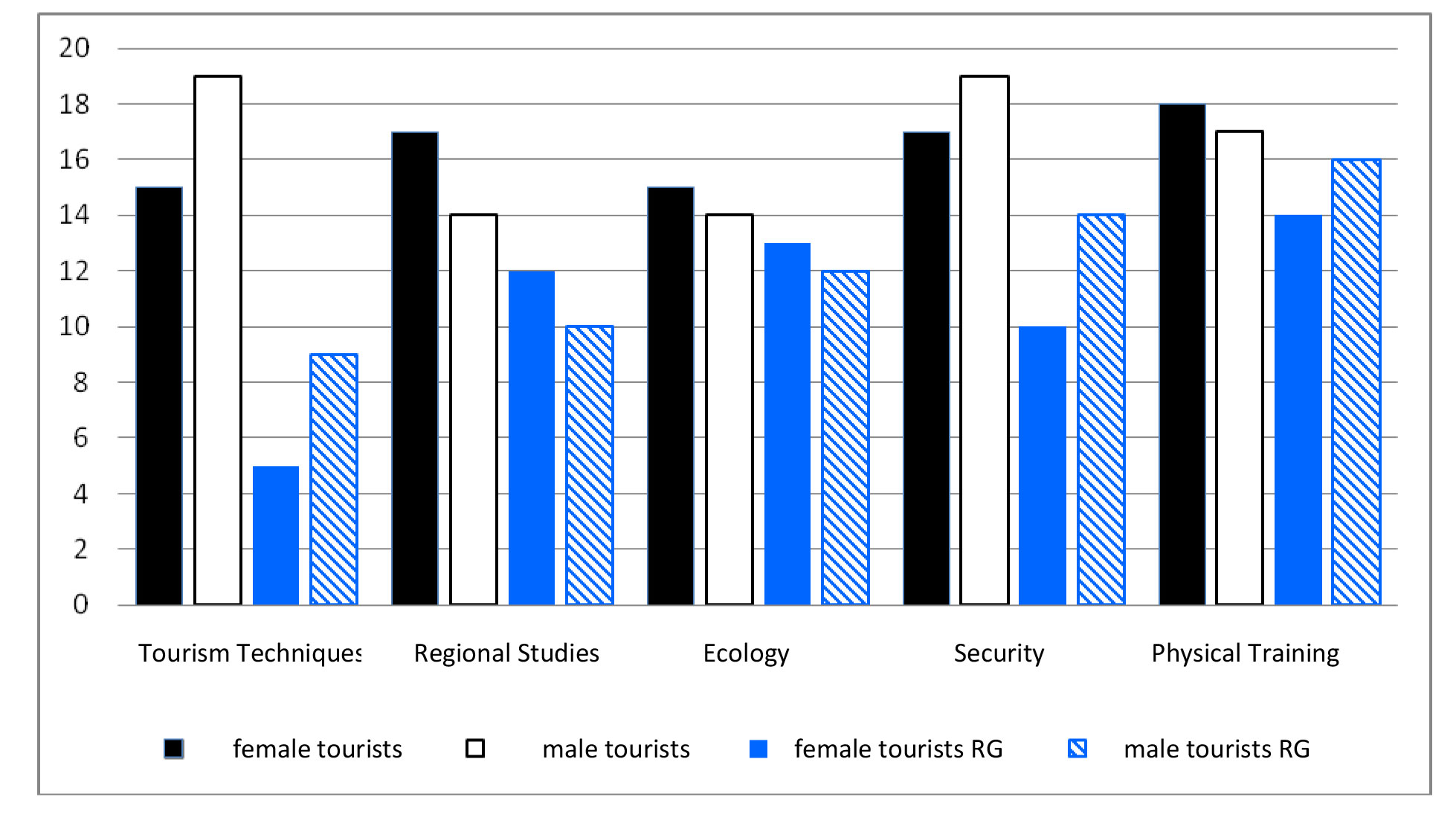
Figure 1. The indicators of formation of competences in thematic blocks
The greatest difference in the formation of competences between the groups was found during testing within the block "Tourism Techniques" - 57.5%. Only a quarter of female students and 45% of male students who were not engaged in sport and health tourism managed to fulfil the main task. In our opinion, this is due to the fact that even those young men who are not engaged in sport and health tourism usually have an experience of solving similar practical problems.
The difference in the formation of competences within the block "Regional Studies" was also significant – 22.5 %. This suggests that sport and health tourism, especially on the territory of a home region, contributes to broadening of the mind regarding the region and the accumulation of knowledge in the field of geography, history and culture of the region.
Ecological competences are an important component, formed in the course of active tourism. The difference between the groups in this block was 10%, indicating the increase of the level of ecological knowledge of students involved in sport and health tourism. These students treat the environment carefully, have the skills of preserving nature and care about the ecology of the region. They consider the aesthetic content of natural resources an important factor of effectiveness of recreation.
The difference between the groups in the block "Security" was 30% (for females – 35%). Sport and health tourism sessions provide mastering of such general competences as the knowledge of fundamentals of health and safety and modern first aid techniques and the ability to survive in extreme conditions.
The difference in the "Physical Training" block did not exceed 12.5%. Despite the fact that the task contained specific elements of sport and health tourism and the level of their complexity can be described as average, most of the students were able to fulfil it. The students engaged in sports and health tourism showed better results in the formation of such competences as the ability to apply knowledge in practice, the ability to work as a team and the ability to identify and solve problems.
Conclusion. The level of involvement of students in recreational activities in Tomsk does not exceed 7% of the total number of students of the Bachelor's degree programs. The study proves the effectiveness of sports and health tourism sessions in the formation of such significant cultural competences as the knowledge of local history and the fundamental of health and safety.
References
- Karvunis Yu.A. Sostoyanie i perspektivyi razvitiya aktivnogo turizma v molodezhnoy srede (Status and prospects of development of active tourism among youth) / Yu.A. Karvunis, L.V. Kapilevich // Teoriya i praktika fiz. kultury. – 2014. – № 10. – P. 62–64.
- Karvunis Yu.A. Spetsifika fizkulturno-ozdorovitelnyih i rekreatsionnyih programm v sisteme detsko-yunosheskogo turizma (Specificity of health and fitness and recreational programs in children's and youth tourism system) / Yu.A. Karvunis, L.V. Kapilevich //Teoriya i praktika fiz. kultury. – 2016. – № 2. – P. 87–89.
- Shil'ko V.G. Fizicheskoe vospitanie studentov na osnove organizatsii obshchestvenno-samodeyatelnyih form fizkulturno-sportivnoy rabotyi v vuze (Physical education of students through organization of public amateur forms of university physical culture and sports activities) / V.G. Shil'ko, N.L. Guseva // Teoriya i praktika fiz. kultury. – 2011. – № 4. – P. 25–27.
- Shil'ko V.G. Pedagogicheskie tehnologii v fizkulturno-sportivnoy deyatelnosti studentov (Pedagogical technologies of physical culture and sports activities of students) / Shil'ko V.G., Shil'ko T.A., Guseva N.L. // Teoriya i praktika fiz. kultury / V.G. Shil'ko, T.A. Shil'ko, N.L. Guseva. – 2014. – № 11. – P. 52–53.
- Brown-Leonardi C. Reindeer champions: culture, rituals and training race reindeer //Polar Record. Jan. 2016. DOI: 10.1017/S0032247415000868
- Humphreys C. Understanding how sporting characteristics and behaviours influence destination selection: a grounded theory study of golf tourism //Journal of Sport and Tourism. 2014, Vol. 19, Iss. 1, P.29-54.
- Kulczycki C., Halpenny E.A. Sport cycling tourists’ setting preferences, appraisals and attachments // Journal of Sport and Tourism. 2014, Vol.19, Iss.2, P. 169-197.
- Yonghuan Hea, Rong Zhaoa, Shuhuai Duana, Maozhu Jina. Intuitionistic fuzzy number: an application to a scenic tourist satisfacation evaluation //Journal of Difference Equations and Applications. Jan 2016, DOI:10.1080/ 10236198.2016.114625
Corresponding author: kapil@yandex.ru
Abstract
Sport and health tourism sessions are an important factor in the formation of general cultural competences of students. This form of recreation is most effective in building such significant general cultural competences as knowledge of local history and the fundamentals of health and safety. Of great importance is also overall physical development, environmental and patriotic education.




 Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE
Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE