Teacher's physical training process design course
Фотографии:
ˑ:
Professor, Dr.Hab. G.N. Blakhin
Professor, Dr.Hab. R.M. Kadyrov
Captain, postgraduate D.A. Solntsev
Major, postgraduate S.A. Antrofikov
Lieutenant Colonel A.V. Gorokhov
Military Institute of Physical Culture, St. Petersburg
Keywords: training, simulation, organizational and management activities.
Introduction. The course of physical training process design for teachers
is carried out within the system of special training arranged at the departments.
The teacher training methodology takes into account the sufficiently high level of their pedagogical readiness and involves appropriate forms and methods of cognitive activity targeted at learners' proactive attitude [3]. Teachers are also provided with the differentiated assistance in organization of the physical training and self-education processes. Active search for assimilation of organization-and-modeling knowledge and skills of teachers is ensured.
Study structure and methods. The initial stage implied choosing basic concepts available in specialized literature, reflecting the essence of simulation process. Basic definitions must reflect organizational aspects. We should note that simulation emerged because of the need to improve the quality of organization and management. Besides, simulation methods help theoretically evaluate various strategies of management process. It is of great importance to include these particular simulation details in the content of education. First, this is connected with the “inner” acceptance of thinking style based on simulation and its significance in enhancing the teachers' organizational and management performance. Thus, each concept was discussed in the context of the need to master simulation for teachers to work successfully.
Results and discussion. At the main stage of determining of the content of education, particular fragments of physical training process simulation, substantiated in the works, were considered [1, 2, 4]. As a matter of convenience of the model presentation and perception, it is relevant to study the block diagrams of physical training simulation fragments.
R.M. Kadyrov has elaborated the training set performance model for air crews (Fig.1).
|
Training set structure |
First level |
Second level |
|
100 m run – recovery time |
16 s 34 s |
17 s 40 s |
|
The beginning of performance Pull-ups – time for exercise – time for recovery |
50 s 16 reps 40 s 60 s |
57 s 12 reps 40 s 60 s |
|
The beginning of performance 3000 m run |
2 min 30 s 13 min 30 s |
20 min 37 s 14 min |
|
Total time |
16 min |
16 min 37 s |

Fig.1. Block diagram of the training set performance
As seen from Fig. 1, training set is repeated until the subjects are able to perform it in the given time-frame. Fig. 2 shows the dependence of probability of performing the exercise set on the quantity of training days.
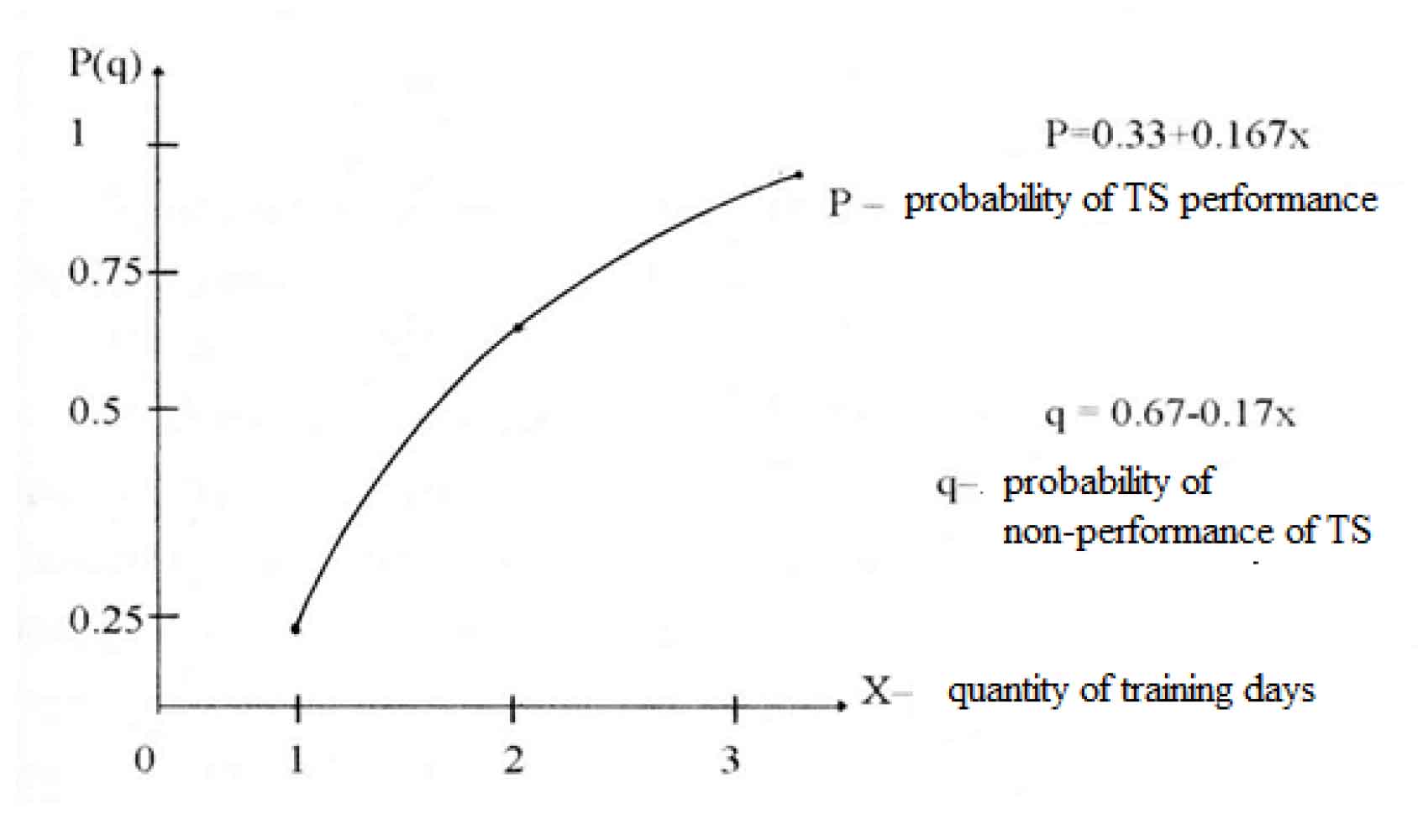
Fig.2. The model of ratio of training set performance and the quantity of training days
This model was added into the content of the educational course for study group teachers.
To study the “duration” of intervals between the physical fitness tests we used the sample designed by R.M. Kadyrov [2]. Moreover, the tests were carried out throughout the academic year, and at the same time, the form, direction and coupling force of various time intervals between the tests (X) and physical fitness level (У) were studied using the 9-point scale. The findings are given in Table 2.
|
Table 2. Dependence of physical fitness level on time intervals between the tests |
||||||||
|
Interval between tests (days) |
Х |
28 |
35 |
42 |
57 |
61 |
78 |
∑ 301 |
|
Physical fitness level (by 9-point scale) |
У |
7 |
6 |
5 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
∑ 30 |
The analytic equation of the dependence between X and У is as follows:
У- 8,61-0,072Х.
Using this equation we can approximately forecast the average rates of physical fitness drop in correlation with the increase of intervals between the routine physical fitness tests. These tables testify to the fact that the level of physical fitness remains stable within the range of 20 to 50 days between the current tests. This model can be used to elaborate the parameters of optimum time duration for retaking the tests. At the same time, it is of great importance to determine time indicators of maintaining a certain level of physical fitness etc. [2].
R.M. Kadyrov notes that the dependence of physical fitness level on duration of endurance training sessions (X1) and the number of actions to assess physical fitness (Х2), is as follows:
У = 6,5 + 1,01X1 +0,5X2, where,
XI and Х2 – the value of encoded factors;
У – the level of physical fitness.
In this case, the model is used to directly analyze the objectives of training sessions and the physical training organization specifics. It is obvious that to solve the tasks of the current study it is necessary to include this model in the content of the teacher's physical training simulation course.
The simplest model of interval (running) load is presented in the block diagram (Fig. 3) [2]. The content of the block diagram is the interval (running) exercise simulation process. The number of the subject and his initial level of MOC (maximal oxygen consumption) are the primary set conditions. Hereafter, the running process at different pace is simulated and the total of energy expenditures of the subject is determined. Note that energy consumption varies depending on the initial level of MOC. Later on, upon acquisition of the experimental data for each subject, statistically average parameters are determined.

Fig.3. Model of running exercise
In the course of training, the reviewed models were consistently included and concurrently adjusted to particular conditions of teachers’ professional activity. Teacher never stops learning when assimilating the physical training organization models, otherwise he cannot develop his creativity.
Conclusions.
Proceeding from the essence of the general relation and interdependence of the current phenomena, we can assume that the correlation between simulation and practice is natural and should be considered when determining the content of education and defining methods of development of teacher’s creativity. The knowledge gained through a simulation process is creatively transformed by the teacher in practice with new and existing knowledge mixed together. With this interrelation in mind the teacher uses methodological advances, innovative teaching methods more quickly and effectively and learns how to generate fresh ideas and assumptions.
References
- Dedov A.E. Organizatsionno-upravlencheskie aspekty sportivno-massovoy raboty v vuze: avtoref. dis. … kand. ped. nauk (Organizational and managerial aspects of university mass sports activities: abstract of PhD thesis) / A.E. Dedov. – St. Petersburg, 1999. – 19 p.
- Kadyrov R.M. Modelirovanie fizicheskoy podgotovki (Physical training simulation) / R.M. Kadyrov. – St. Petersburg: VIFK (MIPhC), 2008. –157 p.
- Potapov R.A. Organizatsionno-upravlencheskaya deyatelnost' prepodavatelya kafedry fizicheskoy podgotovki voenno-uchebnogo zavedeniya: avtoref. dis... kand. ped. nauk (Organizational and administrative activities of physical training department teacher in military institution: abstract of PhD thesis) / R.A. Potapov. – St. Petersburg, 1999. – 19 p.
- Subbot A.N. Normativnye osnovy fizicheskoy podgotovki voennosluzhashchikh MO Ukrainy: avtoref. dis. … kand. ped. nauk (Regulatory basics of physical training of servicemen of DM of Ukraine: abstract of PhD thesis) / A.N. Subbot. – St. Petersburg, 2000. – 18 p.




 Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE
Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE