Courseware for integration of academic and extra-curricular forms of classes for primary pupils based on sports orientation
Фотографии:
ˑ:
Postgraduate student V.V. Yadreev
N.N. Rozhin
A.S. Filippov
V.S. Timofeev
Institute of Physical Culture and Sport of North-Eastern Federal University named after M.K. Ammosov, Yakutsk
Keywords: sports orientation, integration, physical education, pupils.
Introduction. The school subject “Physical education” is the basis of physical education of pupils. In combination with other forms of training – health and fitness and sports activities during a school day the issues of formation of physical culture of an individual are being effectively solved. Important indicators of physical culture of an individual include motivation and the need for systematic fitness and sports sessions, mastering basic fitness and sports activities, good overall fitness [2].
In the Federal laws “On education”, “On physical culture and sports in the Russian Federation”, the Federal target program “Development of physical culture and sports in the Russian Federation in 2006-2015”, “Strategy of development of physical culture and sports in the Russian Federation for the period till 2020”, and in the Concept of development of physical culture and sports in the Russian Federation till 2015 the main task is to ensure health and a high level of physical fitness of the young generation for social and living activities.
Despite this, in recent years extensive research data of scientists (V.K. Bal’sevich, L.V. Volkov, V.V. Gromyko, N.P. Gorbunov, M.G. Ishmukhametov, L.I. Lubysheva, L.N. Progonyuk, V.P. Filin, et al.) indicate that most of the children are lagging behind in terms of physical development, and the number of pupils with various health deviations is growing every year. So it is relevant to search for new methods and forms that would increase the children's motivation in terms of exercising and doing sports regularly [1, 3, 5].
Interaction between general schools and children's and youth sports schools, which takes place under the auspices of the school sports club and solves the problems of sports orientation of children, is the most interesting form of organization of physical education of children.
Most of the researchers consider sports orientation as a process, resulting in the child's choosing a sport that corresponds to his/her inclinations and aptitudes (N.Zh. Bulgakova, A.A. Guzhalovsky, V.M. Zatsiorsky, K.F. Kuramshin, V.N. Platonov, et al.).
Practice shows that in most cases pupils join sports clubs and it is their parents or friends who introduce them into classes. At best, having identified the child's predisposition to specific sport, a teacher of Physical Education advises to engage in a particular sport. Owing to this approach, many of the children engaged in the sports they have no gift for spend time without achieving significant results, leave sport disappointed in it and sports occupations in general. At the same time, if they chose the right sport they could have shown good results.
The purpose of the research is to develop a courseware for integration of school and extra-curricular forms of classes on the basis of sports orientation of primary pupils.
Research methods and organization. The research was conducted at the premises of the Municipal Educational Institution National Polytechnic General School №2 of Yakutsk. Subject to experiment were 68 pupils of 10-11 years of age, including 31 boys and 37 girls. The subjects were divided into two groups: study group – 31 persons, reference group – 37 persons. In the reference group sports orientation was formed using conventional methods of physical education, while in the study group the model of integration of school and extra-curricular forms of physical education on the basis of sports orientation was applied.
Results and discussion. During the research we developed the courseware for integration of school and extra-curricular forms of classes on the basis of sports orientation that provides for synchronization of educational and additional forms of exercises and sport sessions.
The above program was created in view of the functional model of integration of school and extra-curricular forms of physical education lessons for primary pupils we had developed under the premises of the National Polytechnic General School №2 of Yakutsk.
The presented program (Figure 1) makes it possible to integrate school and extra-curricular forms of lessons into the process of sports orientation, which allows to increase pupils’ interest in mastering physical culture values on the one hand and to form educational competences effectively on the other hand.
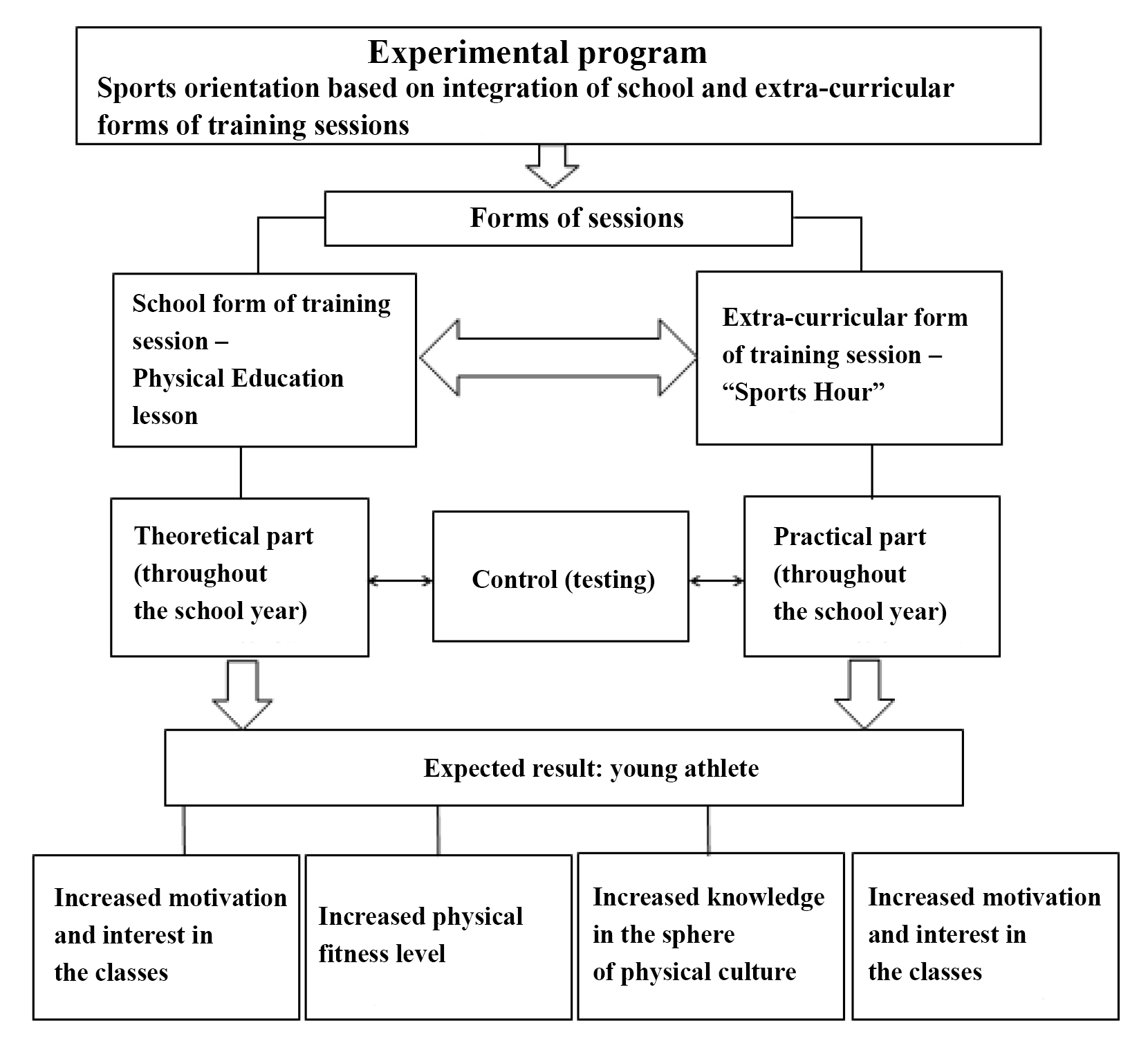
Figure 1. Program for integration of school and extra-curricular forms of physical education lessons for primary pupils on the basis of sports orientation.
During the training we tested multi-media, excursion, school and extra-curricular means aimed at improving the efficiency and quality of characteristics of the educational and extra-curricular process, cognitive activity of the pupils, their mastering of theoretical and methodological knowledge of sports, formation of a mindset oriented at protecting and promoting health, skills and basic motor actions in various sports.
The program included theoretical, practical and control sections.
The theoretical section contained the material for learning about basic sports and modern systems of physical exercises.
The practical section contained physical, competitive and play activities. Effective mastering of this section had an impact on the following indicators:
- formation of motivation and interest in regular physical education and sports sessions as well as in healthy lifestyle;
- reduced incidence rate of pupils;
- improved quality of pupils’ knowledge in the sphere of physical culture and sports;
- improved level of general cultural, social, psychological and specific components of the sports culture of an individual.
The control section contained tests to assess the level of knowledge and physical fitness of pupils by sports.
In addition to these indicators, improved information competence indicates to successful implementation of the program of content and organization of the integration of school and extra-curricular forms of lessons.
Conclusion. The proposed course for integration of school and extra-curricular forms of lessons on the basis of sports orientation made it possible to create most favorable conditions for detecting and developing not only physical, but also mental abilities of primary pupils, help them with self-determination and develop in them the need for regular physical education and sports sessions.
References
- Bal'sevich, V.K. Sportivny vektor fizicheskogo vospitaniya v rossiyskoy shkole (Sports vector of physical education in Russian schools) / V.K. Bal'sevich. – Moscow: Teoriya i praktika fizicheskoy kul'tury i sporta, 2006. – 112 P.
- Kuramshin, Yu.F. Teoriya i metodika fizicheskoy kul'tury: uchebnik (Theory and technology of physical culture: textbook) / Yu.F. Kuramshin. – 2nd ed., rev. – Moscow: Sovetskiy sport, 2004. – 464 P.
- Lubysheva, L.I. Sportivnaya orientatsiya: novy vektor razvitiya (Sports orientation: new vector of development) / L.I. Lubysheva, T.A. Polyakova // Fizicheskaya kul'tura: vospitanie, obrazovanie, trenirovka. – 2009. – № 1. – P. 2–6.
- Matveev, A.P. K probleme soderzhaniya obrazovaniya po fizicheskoy kul'ture v kontekste trebovaniy standarta vtorogo pokoleniya (Content of physical culture education in context of second-generation standard requirements) // A.P. Matveev, Yu.I. Razinov // Teoriya i praktika fizicheskoy kultury. – 2009. – № 6. – P. 53–57.
- Filin, V.P. Teoriya i metodika yunosheskogo sporta: ucheb. posobie dlya institutov i tekhnikumov fiz. kul't. (Theory and technology of youth sport: study guide for institutions and colleges) / V.P. Filin. – Moscow: Fizkul'tura i sport. – 1987. – P. 128.
Corresponding author: yadruk@mail.ru




 Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE
Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE