The problem of unification of conceptual framework of innovative health technologies
Фотографии:
ˑ:
Yu.P. Kobyakov, associate professor, Dr.Hab.
A.V. Bolotov, candidate
Vladimir State University named after Alexander and Nikolay Stoletovs
Keywords: genesis, etymology, development, training, upbringing, formation, education, innovative health technologies.
The idea of necessity to promote human health does not belong to the category of “know-how”, and during the last century it has been viewed as a national objective in our country. The Ministry of Health has been realizing the objective, and one of its most important functions is the maternity and childhood protection.
However, the deterioration of health of people around the world, including Russia, in the last quarter of the 20th century, required taking additional and appropriate measures to stabilize and improve the situation by all state social institutions. A set of special programs such as “Protection of Childhood”, “Health of the Nation” and others have been developed at the state level. The idea of the necessary transition of the educational system to the teaching and training of the younger generation on the basis of technologies aimed at promoting and protecting of the student health has matured in the pedagogical community.
The terms of health-promoting, health-protecting and health-forming technologies, and later a health-developing technology were positioned in the terminological database [1]. In point of semantics, the name of any technology is a compound adjective with the root “health”. The second root of the term is an adjective showing the direction of the pedagogical influence on the educational process. Unfortunately, the terms above are often used not in the connection with the methodology of pedagogical activities, but they are used in scientific publications, outside of the context and content of the actual material; they are used by way of imitation of other authors because the usage of such terms has become rather popular. Lots of similar in sound terms create certain difficulties in their interpretation and further usage, thus causing logical and inevitable reference to genesis and etymology of pedagogical terms. A.N. Ryzhkov emphasizes that the undeveloped problem of genesis of the terms is becoming a hindrance in the development of the pedagogical theory [5]. The definition of the etymology of terms and appropriate usage of them are finally a fight for broadening of vocabulary, for purity of Russian language, for the standard of speech in the social and pedagogical spheres.
Let us dwell on the genesis of terms, which have designated to the technologies of the same names – promotion, saving, development, formation.
An explanatory dictionary of the Russian language shows that the terms “promotion” and “saving” are synonyms that mean the necessity of keeping something in the memory, not to forget something, not to let something be lost, to promote the integrity of something that has been collected earlier. The word “promotion” has the same content as the word “protection”. Protection means defending something or somebody using some outside force. As applied to the educational process, this understanding of the term theoretically can be applied to the name of health-protecting technology, by analogy with the name of the Ministry of Health. However, in the terminology of pedagogics the term is used more euphoniously – health promotion. As we see, it is no more than word-play. Still the term “health care” is steadier and more often used in pedagogics at the moment. In our understanding the term “saving” is the category which is wider than the term “promotion”. This category comes laden only with the stable features of biological order, which become apparent in prophylaxis, promotion and protection of health, but also socially significant determinants laying in understanding of imperishable value of individual health which is the basis of our nation’s prosperity and well-being.
In an explanatory dictionary the term “formation”, which names one of the listed technologies, means giving shape and form to something or cultivating definite character traits of an individual. We believe, the concept “personality formation” can be viewed to narrow and wide extent. A narrower idea of formation is inherent in the modern pedagogical theory. The theory regards the formation from the point of view of a person’s coming-to-be as a social creature under the influence of the whole complex of personal-forming factors. Formation implicates completeness of a human personality, achievement of the level of maturity and steadiness ([3], – p.28), and we must realize that this formation comes to an end with finishing of professional education and a person’s inclusion into the system of social relationships.
In a wider sense, personality formation is an objective biological and natural social process, in the course of which a person is not only an object of influence, but also a subject of activity and communication throughout the vital cycle.
The given definitions point at the direct connection of new terms with the objective existence of three natural phenomena – development, promotion and formation, which are categorically reflected in the philosophical concepts of the same name.
The well-known dialectical law implies that the promotion of the sociocultural potential, that has been acquired in the previous years, and the personality formation take place in a person who has high motivation, settled opinions about social norms and values of life at every convolution, when his mental sphere is developed and improved.
There are five pedagogical categories in the conceptual apparatus of the pedagogical theory which are as follows: training, education, upbringing, development, formation (Fig. 1) [3]. The presentation of categories in a two-dimensional coordinate system causes the dilemma, related with a vector that can be chosen to look at the picture. If we look at it according to the logic of the educational process, the vector will be from top to down.
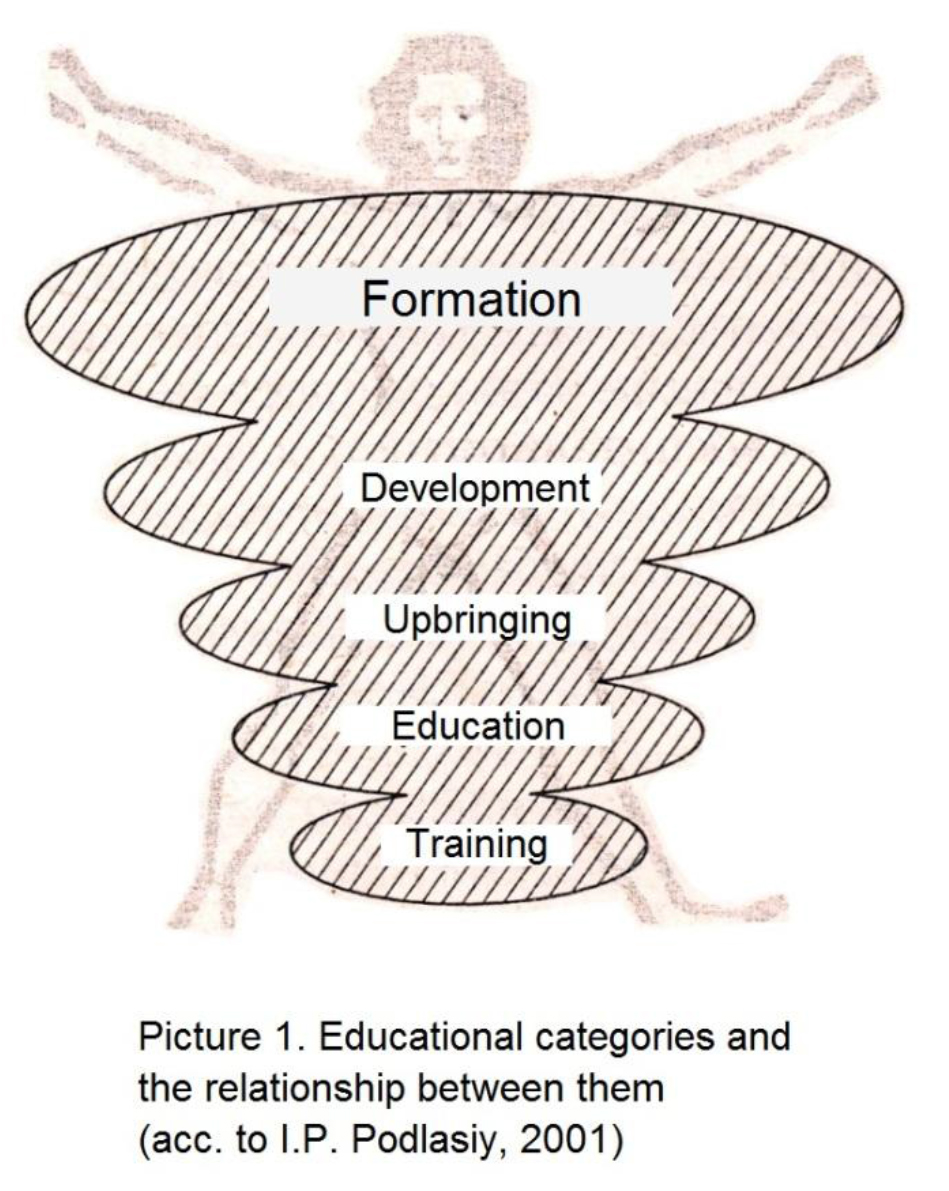
The picture shows that the two pedagogical categories – development and formation – have the distinct biological basis and have become the formative elements of the innovative health technologies of the same name, and that is absolutely well-taken. Here we mean that the dialectical unity of person’s biological and social origins is reflected in the notions of the pedagogical categories. At the same time it should be noted that the term “development” was used by one of the co-authors of the article to prove the conception of the health-developing technology, as an individual subject (according to G.K. Selevko’s classification) [5], which is realized predominantly in the context of the subject “Physical Education” [1].
Due to the ever-growing number of technologies [5], we can forecast in the long term an appearance of “health-training”, “health-educational” and “health-educative” technologies, if we rely on the semantic range of pedagogics further. For example, we can see the definite features of this approach in the A.G. Madzhuga’s work, who has suggested the “health-creating” technology in the scientific community [2].
However, taking a closer look at the problem, it becomes clear that the appearance of new technologies, in the names of which the notions of the pedagogical technologies such as training, education, upbringing could be used, is possible only theoretically, and unlikely practically, because the two processes out of three – training and upbringing – are realized in the indissoluble unity with development and promotion of the accumulated potential of health and perfection of personality.
The question about implication of the category “education” into the given scheme is worth special discussing. Each of the four categories – training, upbringing, development, and formation – implies one of the educational functions. The concept “education” in this context has the collective sense and must be viewed, on the one hand, as a special form of organization of the pedagogical process, that is directed towards gaining necessary knowledge and skills by students, and on the other hand, as a result of these actions. Taking into account these ideas, the presentation of “education” as a category of pedagogics in the given picture is, from our point of view, not quite reasonable. In our ideas, the category “development” must be generalized, meaning the basic significance of this function, comprising not only the process of natural accumulation of vital potential by students, but also gaining a personal-creative status by an individual.
The approximation of the existing pedagogical models indicates that the latter are static as their image plane is two-dimensional, and it does not reflect the integrity of the vital cycle of personal development. In this connection the authors have to use additional graphical methods (connected and dotted lines, arrows and so on).
On the basis of the produced logic-content analysis, the hierarchical structure of the educational process and interconnection between the categories of this structure can be represented, in our ideas, as in Figure 2. Designing the given model, we relied on the original basis of the philosophical human theory – activity, consciousness, personality [6]. In this work we examine and discuss the processes and phenomena only in the context of the activity theory. Let us compare the structures of models in Figures 1 and 2.
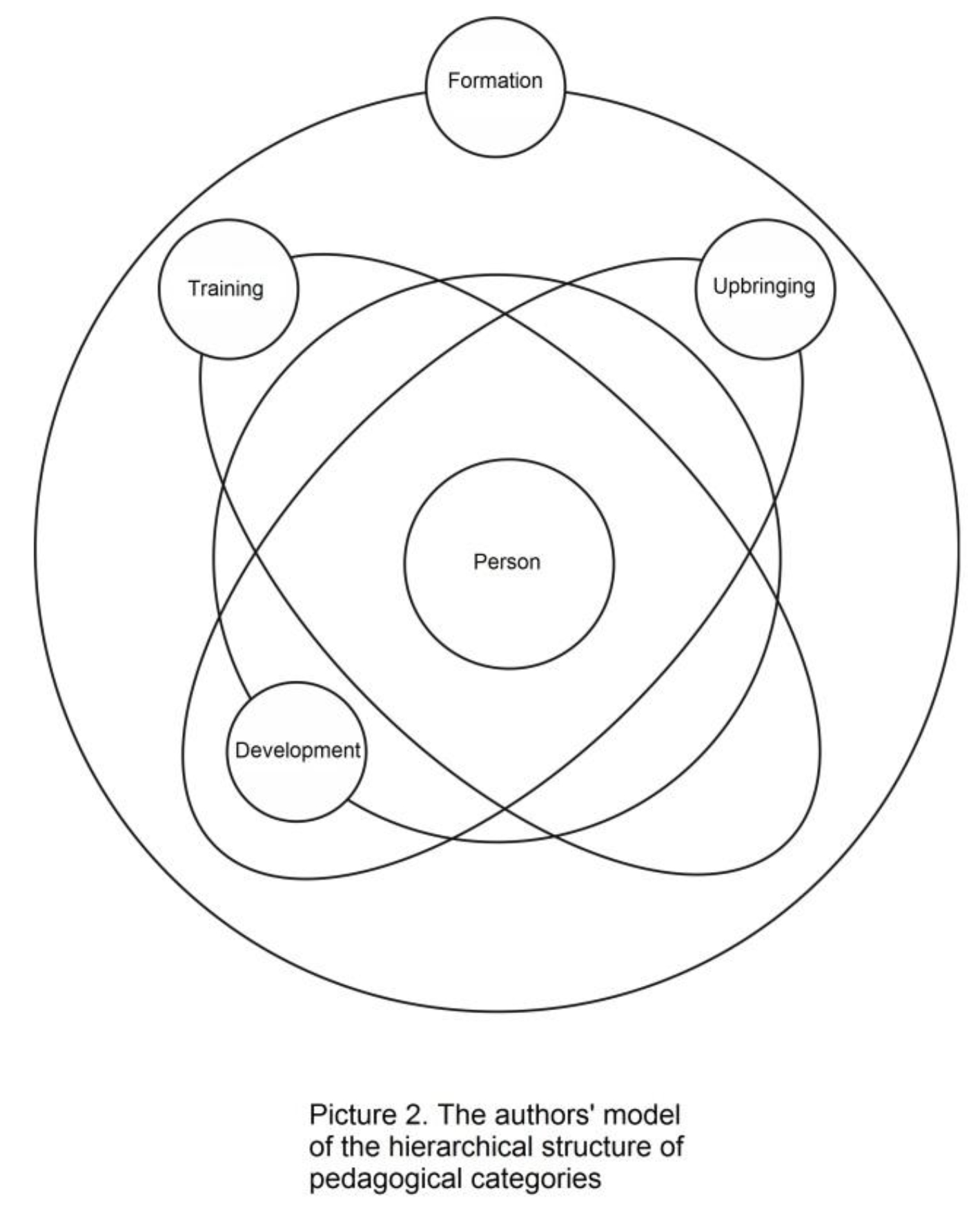
In Figure 1 the pedagogical categories look quite static, and the interconnection between them line up only vertically. In Figure 2 the structure and interconnection between the categories look like the three-dimensional planetary system which is on the constant run round the nucleus – the centre of the system, and person is an object and a subject of educational activities in this centre. There are four rings at different distances around the nucleus, around which the factors of influence or the elements of the system are constantly moving – development, training, upbringing, formation. At the same time the influence of some individual elements of the system on the object of education grows as they approach the center. The category “development” in the discussed scheme is situated closer to the center of the model, to its nucleus, as development is much more important for settling the problems of the educational process, than training or upbringing, which are situated at the periphery. Development is a basis, in which the anthropological grounds of human personality are reflected. Simultaneously development is the backbone category including the processes of training and upbringing. At the same time the process of development is objective and is caused by the subject-activity essence of the personality.
If we continue this comparison with the satellites, it is necessary to make a slight clarification and say that in this case, they (the satellites) have no stationary orbits. Their trajectories remind floating satellites more, as this or that of them can be closer to the center of the nucleus at every given moment of time, depending on a situation, but development is major in general.
On the one hand, we accentuate the intensity of interconnection and interference between these processes by comparing the processes of development, training, upbringing and formation with the satellites, and on the other hand, we accentuate the possibility of mental dismemberment of the object into separate parts, elements and integration of them, that to the full extent meets one of the other requirements of the systems approach.
The idea of tridimensionality, which is taken as a structural principle of the model, emphasizes dynamism of the system and availability of potential of its development, which in particular, manifests itself in “the systemic effects”; their feature is the appearance of new properties of the system as a result of interconnection of the elements in the context of the whole.
Our logical-content analysis, based on the modern ideas of the scientific-rationalist philosophy, and the semantic analysis of some structural units of the pedagogical conceptual framework let us conclude the following.
Appropriation and usage of the notions of the innovative health technologies are determined by the complex combination of the biological and social factors.
In our opinion, the positioning of three relatively independent technologies– health-developing, health-promoting and health-forming – is preferable in the pedagogical terminology.
The term “saving” implies the widest collective sense, it reflects the social importance of the influence to a greater extent than “promotion”, and the influence is directed at keeping the life potential, have been collected in previous years. In this context the health-saving technology becomes “the leading variable” and unites the other technologies, including all the above-listed. Consequently, the name of the given technology should be used in plural – “health-saving technologies”.
References
- Kobyakov, Yu.P. Proektirovanie i realizatsiya zdorov’erazvivayuschey tekhnologii fizicheskogo vospitaniya studentov vuzov (Design and implementation of health-developing technology of physical education of higher school students): doctoral thesis (Hab.). – Moscow, – 2006. – 350 P.
- Madzhuga, A.G. Pedagogicheskaya kontseptsiya valeologicheskoy funktsii obrazovaniya (Pedagogical Concept of Valeological Function of Education): doctoral thesis (Hab.). – Vladimir, – 2010. – 385 P.
- Podlasiy, I.P. Pedagogika. Novy kurs. (Pedagogics. New Course). Book 1. Fundamentals. Educational process. – Moscow: Vlados. – 2001 (1996). – 576 P.
- Ryzhov, A.N. Genesis pedagogicheskikh terminov v Rossii (XI – nachalo XXI v.) (Genesis of pedagogical terms in Russia (XI – early XXI): doctoral thesis (Hab.). – Moscow, – 2013.
- Selevko, G.K. Sovremennye obrazovatel’nye tekhnologii (Modern Educational Technologies): Tutorial for teacher training institutions and Institutes of Professional Development. – Moscow: Narodnoe obrazovanie. – 1998. – 256 P.
- Frolov, I.T. Vvedenie v filosofiyu (Introduction to Philosophy). – Moscow: Publishing house of political literature. – 1990. – 640 P.
Corresponding author: vip.mr.strannik@mail.ru




 Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE
Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE