Concentrated training technology for academic elective aerobics
ˑ:
PhD, Professor K.N. Dementiev1
PhD, Associate Professor E.G. Zuykova2
PhD, Associate Professor T.V. Bushma2
PhD, Associate Professor O.N. Ustinova2
PhD, Associate Professor I.I. Kiprushina3
1St. Petersburg State University of Civil Aviation, St. Petersburg
2Peter the Great Saint Petersburg Polytechnic University, St. Petersburg
3Herzen State Pedagogical University of Russia, St. Petersburg
Keywords: aerobics, concentrated training, technology, students, physical education, healthy lifestyle.
Background. Concentrated training may be defined as a special intensive education technology that requires the students to fast process and master the learning materials well-structured and classified within the timeframe of the regular curriculum. Essentially the concentrated training prioritizes the cognitive process continuity and integrity to: facilitate comprehensive learning; encourage students’ independence and creativity; offer a wide variety of combined applied training methods and tools; and encourage cooperation of trainers and trainees [1, 2]. As far as the variety of modern concentrated training models tools is concerned, of special interest are the concentrated training application methods to supplement the academic physical education discipline. Elective aerobics course to supplement the physical education discipline offers high promises for practical concentrated training models since the modern physical education service prioritizes the mandatory variability of physical education classes conditional on the physical education service being harmonized and integrated.
Objective of the study was to develop and test benefits of an elective concentrated-training-based aerobics model to meet requirements of the progressive physical education service concept for students’ physical progress in practical aerobics trainings.
Methods and structure of the study. We consider concentrated training among the highly promising modern innovative training methods due to its special benefits for the education service quality since the concentrated training:
- Helps harmonize and integrate the education service elements;
- Facilitates the learning process putting it on a sound and systemic basis since the learning material is offered in logical and complete modules/ units;
- Encourages motivations for trainings;
- Develops comfortable psychological climate due to the cooperative training service design with a special priority to the individual needs and progress agendas of the trainees; and
- Puts the training process on an individualized basis, with every student offered an individual progress trajectory [1-3].
The concentrated-training-based aerobics course was designed to include the following modules. Information module gives a theoretical knowledge of the training process design and management logics, elements and basics, physical qualities progress regularities; key muscle groups; and the aerobics benefits for a healthy lifestyle cultivation purposes. Diagnostics module is designed to test and analyze the physical fitness, performance, functionality and psycho-emotional health of the trainees. Content module systematizes the knowledge, target motor skills and practical progress benchmarks to encourage motivations for habitual physical activity and healthy lifestyle. Self-reliant training module includes the teacher-consulted practices on an independent basis, with or without preliminary trainings, as provided by the relevant practical guidelines with the theoretical basics and special self-training tasks. And the control module offers a test set with the pre-training, interim and post-training tests for the progress control for the whole training period.
The above modules are designed to facilitate their integration in the concentrated-training-based course to ensure new quality for the training process, with every trainee making progress in the physical fitness, functionality and psychological fitness for a fully-fledged socializing process and future professional service. The modules offer reasonably integrated theoretical and practical training materials for the self-reliant progress with the systemic progress tests for the training system adjustments. The new concentrated-training-based aerobics model to supplement the academic physical education discipline was tested on the 1-2-year students.
The concentrated-training-based aerobics model with its harmonized modules secures the educational process integrity with due “immersion” of trainees and staged learning. The concentrated-training-based aerobics model was implemented on the following provisions:
- Cooperative efforts of the teaching team highly knowledgeable and skilled in the aerobics training models and tools;
- User-friendly access to the educational materials supported by the modern information technologies; and
- Integration of the training theory and practice, with a synthesis of knowledge and skills.
The trainees’ progress in the concentrated-training-based aerobics model was tested by the test tables for the functionality and physical progress rating purposes in the self-reliant and creative trainings [4-6], with the model benefits tested in the 1-2-year physical education classes.
Results and discussion. Given on Figure 1 hereunder are the progress test rates of the sample in the concentrated-training-based aerobics model testing experiment.
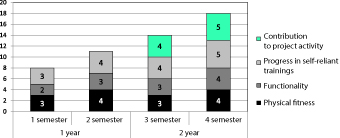
Figure 1. Progress test rates of the sample in the concentrated-training-based aerobics model testing experiment
The final progress tests found the 1- and 2-year groups physical fitness growing by 19% and 23% and functionality growing by 21% and 18%, respectively; with 92% of the sample tested with a high ability to apply the knowledge, skills and competences in the self-reliant trainings, creativity-intensive tasks and project activities.
New training model benefits were tested, among other things, by a questionnaire survey of the sample to obtain the respondents’ opinions on the concentrated-training-based aerobics model design and content. The survey found 95.9% of the sample satisfied with the model; 82.8% highly interested in the concentrated-training-based aerobics service; and 77.8% looking forward to continue the trainings in the 3rd academic year. It should be also mentioned that the survey found the following drawbacks of the model:
- Fast accumulation of the training backlogs in case of grounded absences in a few training sessions;
- Still limited room for application of modern computer technologies to facilitate preparations for the practical trainings; and
- Shortage of visual practical guides and recommendations on the screens to support the trainings.
Conclusion. The new concentrated-training-based aerobics model with its innovative high-intensity education technology was found beneficial as it gives the means to put the physical education service on a balanced and multidimensional basis for permanent progress, and customize the trainings to the individual needs, skills and progress agendas. The new concentrated training technology was tested particularly beneficial for the aerobics trainings in large groups, with the practical sessions designed on a non-stop basis to ensure the time-efficiency within the academic physical education curricula, rapidly build up the theoretical knowledgebase and skill sets, meet the valid requirements to the physical education service permanence and integrity; effectively meet the individual physical progress needs of the students; motivate them for physical activation and progress; and establish a comfortable training climate for productive cooperation of the training service staff and trainees.
References
- Ibragimov G.I. Concentrated training: Theory, History, Practice. Kazan: Tsentr innovatsionnykh tekhnologiy, 2010. 364 p.
- Neudakhina N.A., Panin A.V. Application possibilities for concentrated training technology in higher education. Quality Assurance of Professional Education: Proc. International res.-practical Conference, April 25 2019: ASTU publ.. Barnaul, 2019. pp. 128-131.
- Gitman E.K., Khlybova M.A. Concentrated learning of foreign language in non-linguistic university. Perm: Prokrost publ., 2014. 135 p.
- Bushma T.V., Volkova L.M., Zuykova E.G. Organization and Content of Independent Work of Students Specializing in Aerobics. Teoriya i Praktika Fizicheskoy Kultury. 2015. no. 2. pp. 24-26.
- Bushma T.V., Zuykova E.G., Volkova L.M. Creative self-realization of students in aerobics classes. Kultura fizicheskaya i zdorovye. VSU publ.. 2018. no.3 (67). pp. 100-102.
- Mironova O.V., Tokareva A.V., Moskalenko I.S. et al. Forming self-reliant aerobic training process management skills for success in examinations. Teoriya i Praktika Fizicheskoy Kultury. 2016. no. 9. pp. 12-15.
- Lukina S.M., Mironova O.V., Sharonova A.V. et al. Innovative technologies for academic physical education and sport service. Teoriya i Praktika Fizicheskoy Kultury. 2019. no. 4. pp. 44-46.
- Yarchikovskaya L.V., Tokareva A.V., Mironova O.V. et al. Healthy lifestyle promotion in academic physical education process. Teoriya i Praktika Fizicheskoy Kultury. 2018. no. 2. pp. 85-87.
- Zuykova E.G., Bushma T.V., Lipovka A.Yu., Cherkasova A.V. The Usage Of Modular-Rating Technology In The Educational Process Of Physical Culture. The European Proceedings of Social &Behavioural Sciences EpSBS. Published by the Future Academy. 2018. Volume LI pp.127-133.
Corresponding author: dementevkn2013@yandex.ru
Abstract
Objective of the study was to develop a concentrated training technology that would enable to implement the principle of continuity of the training process and ensure an in-depth study of the discipline during aerobic practices.
Methods and structure of the study. The study involved monitoring of the effectiveness of the developed concentrated training technology, determination of the degree of adaptation of the 1st- and 2nd-year students to the proposed model during the aerobic practices, as well as a comprehensive assessment of the quality of training.
Results of the study. The final test results revealed a high level of knowledge, practical skills, ability to make use of the acquired competencies, positive dynamics of the students' physical, functional, psychoemotional test rates.
Conclusion. Concentrated training as a pedagogical technology, being one of the intensive teaching methods, enables to create balanced in content multilevel models of continuing education and implement them in the aerobic training programs, to build a learning path based on the individual characteristics of students.



 Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE
Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE