Academic physical fitness rating by gto complex tests
ˑ:
PhD, Associate Professor A.V. Voronkov1
PhD, Associate Professor I.N. Nikulin1
PhD, Associate Professor A.A. Kolesnikov1
D.E. Nikulina1
1Belgorod State National Research University, Belgorod
Keywords: Russian Physical Culture and Sports “Ready for Labour and Defence” (GTO) Complex, Belgorod State National Research University, students’ physical fitness, academic progress .
Introduction. The GTO Complex, being the program and normative basis of the physical education system in Russia, involves more and more participants. Obviously, it is educational organizations that ensure the greatest involvement in the Complex activities. The large-scale implementation of the Complex in educational organizations contributes to both assessment of the students’ physical fitness level and creation of the necessary conditions for regular and systematic physical education activities, increment in the targeted motor activity and health promotion. Therefore, effective implementation of the GTO Complex is one of the most important problems that the administrative and teaching staff of any higher education institution faces. Implementation of the Complex in the format of competitions contributes to greater involvement of all potential participants in these events.
Objective of the study was to analyze the GTO Complex test results of students at the university level.
Methods and structure of the study. In December 2018, the first Russian GTO Complex student festival was held as part of the project “GTO badges for academic progress”. The project was carried out at three levels: university, regional and national.
Sampled for the GTO Complex year- and gender-specific tests were the Physical Education Department students (n=175, including 104 young males and 71 females). When rating the male and female students’ physical fitness level, we analyzed their test results during various years of study.
Given that the GTO complex implies both mandatory and optional tests, we assumed that the number of students qualified for a badge would correspond to the potential number of badge holders.
Table 1. The number of male students of the Physical Education Department qualified for the badge
|
Year of study |
Participants |
Qualified for a badge |
% |
|
1st |
28 |
9 |
32.1 |
|
2nd |
22 |
5 |
22.7 |
|
3rd |
23 |
1 |
4.3 |
|
4th |
31 |
14 |
45.2 |
|
Total |
104 |
29 |
28 |
Table 1 shows that 28% of male students were able to qualify for the GTO badge. The analysis of the data, divided up by the year of study, revealed no downward tendency in the level of physical fitness from year to year. There was a sharp decrease in the indicators during the 3rd year of study, followed by a significant increase during the 4th one. Apparently, this was due to the individual characteristics of the students.
Table 2. The number of female students of the Physical Education Department qualified for the badge
|
Year of study |
Participants |
Qualified for a badge |
% |
|
1st |
20 |
7 |
35.0 |
|
2nd |
16 |
6 |
37.5 |
|
3rd |
18 |
6 |
33.3 |
|
4th |
17 |
9 |
52.9 |
|
Total |
71 |
28 |
39.4 |
The number of potential badge holders among the female students equaled almost 40% (which exceeded the number of male students by 12%). Moreover, as with young males, their physical fitness rates andyear of study did not correlate with each other (Table 2).
It is obvious that less than half of the Physical Education Department students were able to qualify for the GTO Gold badge. Given that the students studying at this faculty have the highest physical fitness level, it can be stated that the GTO Complex badge standards are definitely characterized by an adequate level of complexity, and receiving a badge suggests a high level of man’s physical fitness.
Results and discussion. The analysis of certain mandatory GTO Complex test results showed that 94% of young males and 100% of females successfully qualified for the badge, which implied a high level of development of their speed qualities.
About 90% of male and 80% of female students successfully qualified for the badge characterizing a high level of development of their strength qualities. It is obvious that it is females who were most successful in the strength tests.
The flexibility test “Standing bends forward on an exercise bench” showed that 85% of young males and 93% of females had sufficiently developed flexibility as required by the GTO Complex.
Therefore, it can be stated that the GTO Complex tests to determine the level of development of speed, strength qualities and flexibility usually are not difficult for most of physically fit students.
Evidently, the endurance tests were the most difficult for the students. The analysis of the 2 km and 3 km run test results showed that this test was chosen by the smallest number of participants: 78 young males (75% of test participants), and 46 females (65% of test participants). The number of students qualified for the badge in this test was significantly lower than in other tests. Thus, 49% of young males and 87% of females were able to qualify for the badge in the 3 km run test.
Figures 1, 2 illustrate the results of each of the mandatory GTO Complex tests, as well as the 4 mandatory test results.
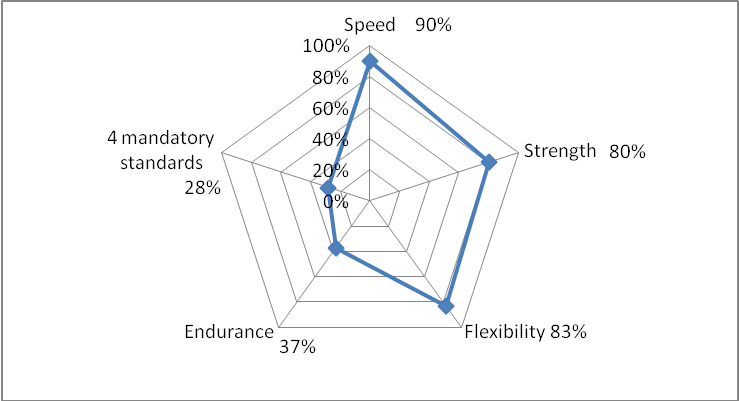
Fig. 1. Mandatory GTO Complex test results of Physical Education Department male students
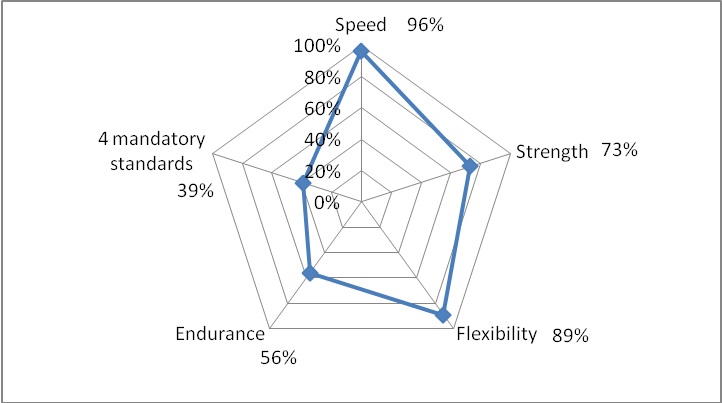
Fig. 2. Mandatory GTO Complex test results of Physical Education Department female students
Conclusions. The analysis of the test results allowed for the following conclusions:
- nearly 30% of male and 40% of female students of the Physical Education Department are able to qualify for the GTO Gold badge;
- there is almost no difference in the physical fitness level of students of different years of study;
- it is the endurance tests (2 km and 3 km run) that pose the greatest difficulties for students;
- successful qualification for the GTO Complex standards testifies to the high physical fitness level and versatile physical development of students of the Physical Education Department.
References
- O fizicheskoy kulture i sporte v Rossiyskoy Federatsii [Physical education and sports in the Russian Federation]. [Electronic resource]: Feder. law Dec 04 2007 # 329-FZ (as am. on 29.07.2018)]. Reference legal system "Consultant Plus". Available at: http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_73038
- Ob utverzhdenii gosudarstvennykh trebovaniy Vserossiyskogo fizkulturno-sportivnogo kompleksa «Gotov k trudu i oborone» (GTO) na 2018-2021 godyi [On the approval of state requirements of the Russian physical culture and sports complex "Ready for Labor and Defence" (GTO) for 2018-2021]. [Electronic resource] : Prikaz Minsporta Rossii ot 19 iyunya 2017 # 542 [Decree of the Ministry of Sport dated June 19 2017 #542]. Federal portal «GTO.RU». Available at: https://www.gto.ru/files/uploads/documents/596851c7b6aea.pdf
Corresponding author: voronkov@bsu.edu.ru
Abstract
The given study was intended to test and analyze the Belgorod State National Research University students’ physical fitness by the Russian Physical Culture and Sports “Ready for Labour and Defence” (GTO) Complex test standards. Sampled for the GTO Complex year- and gender-specific tests were the physical education Department students (n=175, including 104 young males and 71 females). The test data analysis found the following: (1) About 30% and 40% of the male and female groups (respectively) were successful in the tests to qualify for a GTO Complex badge; (2) Physical fitness test rates were virtually year-unspecific; (3) Most difficult for the sample were the endurance-rating 2/3km race tests; (4) The relatively high success rate in the GTO Complex tests was indicative of the fairly good physical fitness and versatile physical development of the physical education Department students.



 Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE
Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE