Game performance basics mastering training for beginners
ˑ:
Associate Professor, PhD N.V. Lutkova1
Dr.Hab., Professor Y.M. Makarov1
Associate Professor, PhD A.A. Ramzaytseva1
E.I. Mokina1
Dr.Hab., Professor A.A. Zaitsev2
1Lesgaft National State University of Physical Education, Sport and Health, St. Petersburg
2Kaliningrad State Technical University, Kaliningrad
Keywords: primary skills, game basics, long-term training process, team sports.
Background. The national elite sport system gives a special priority to the sport reserve training policies and practices [3], with the new sport-specific training methods and model increasingly requiring sound research, theoretical and experimental developments for progress. Thus the Y.M. Makarov’s [1] multiannual game framework mastering method is driven by a special progress securing algorithm that includes the following three progress stages: game basics mastering; competitive game trainings; and game excellence/ mastery training.
We have addressed in our study the first of the above stages i.e. the game basics mastering framework that should, as we believe, make a special emphasis on the individual process reference points, with the selection options being as wide and versatile as possible to encourage individual gifts. Junior athletes are expected to identify on their own the reference point in every game situation to independently analyze and find the best solutions. The training process driven by this logic is geared to encourage the best individual game control toolkit formation in every player. We give a high priority to this approach since the traditional beginner training practices are dominated by the game technicalities mastering practices and largely limit the individual progress in the game vision, tactics and other aspects; with the underdeveloped individual game vision/ control skills resulting in the competitive failures and underperformances, with the game quality on the whole falling short of the modern expectations, game standards, trends and requirements.
Objective of the study was to develop a game basics mastering training algorithm for beginners to help them acquire the primary technical/ tactical skills for success in the long run.
Methods and structure of the study. A top priority in our study was given to the game basics (guiding framework) mastering by the beginner players with a special emphasis on the game vision i.e. the ‘situational orienteering’ aspect, with the relevant game vision training system rather specific in the design and contents. The situational orienteering/ control focused training may be interpreted as the process to excel the space/ time/ muscular effort/ sensor-motor response qualities, develop the cognitive abilities, motor memory and the situation-specific game controls or responses. The three-year study (01.09.2015 to 31.05.2018) was run in practical CYSP (Children and Youth Sport School) training processes in team sports within the relevant education/ training curricula, with 34 coaches engaged in the study process.
Results and discussion. The game basics mastering process for beginners was designed to offer accessible elementary game practices within a certain game guiding framework – which may be defined as the mental control mechanism for the sensorimotor responses that activate the relevant execution/ control operations. This mental control mechanism is formed at the following three levels: sensor-perceptive; verbalized logical; and the individual behavioral ones, with a transition from the ‘sensational’ level to the ‘intellectual’ level going via a good understanding of the movement logics and outcomes colored by the individual semantics – and this is how the integral game vision concept may be briefly outlined [2]. It should be noted that the game framework (basics) is rather complicated and rich in content in fact. This is why the game basics mastering process will concentrate on the following three basic domains: external vision (‘orienteering’); internal vision control; and the result vision trainings.
Therefore, the beginner game basics mastering trainings need to be facilitated by the versatile educational provisions to secure progress in every of the three above mastery domains. It should be emphasized, however, that the training system should be rather sensitive to the individual overall/ specific physical and mental fitness for the game – in view of the fact that the traditional beginner trainings normally pay little if any attention to this aspect. It is quite typical for many coaches to require the beginners being highly sensitive to every game situation, well control it and forecast outcomes of every action – and tend to believe that such an inclusive approach facilitates the game technicalities mastering process. This overloading approach, however, often turns out detrimental for the individual progress and results in chronic tactical/ tactical deficiencies found in the later training stages.
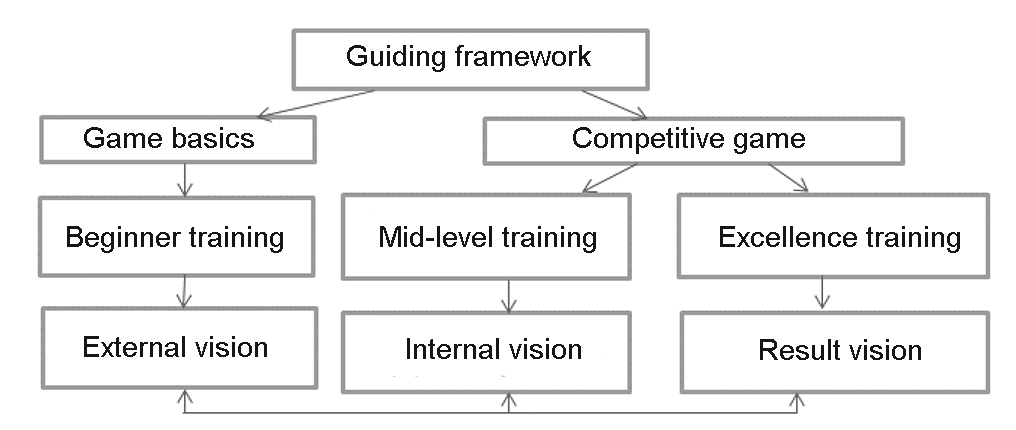
Figure 1. Game guiding framework formation sequence in a long-term junior training process
The game basics/ guiding framework mastering process in the long-term junior trainings may be facilitated when designed as a logical sequence of actions (see Figure 1), with the best progress in the game vision developing practices achieved when the guiding framework is always respected and reminded in every training stage. This sequence is critical for every stage in a multiannual training process – for instance, the beginner training shall give a top priority to the external vision with a reasonable attention to the internal vision and the least attention to the result vision. Our study gives a special consideration to the guiding framework development trainings at the beginner training stage with its focus on the external vision/ orienteering qualities. We believe that the external vision mastering process shall be designed as follows: see Figure 2.
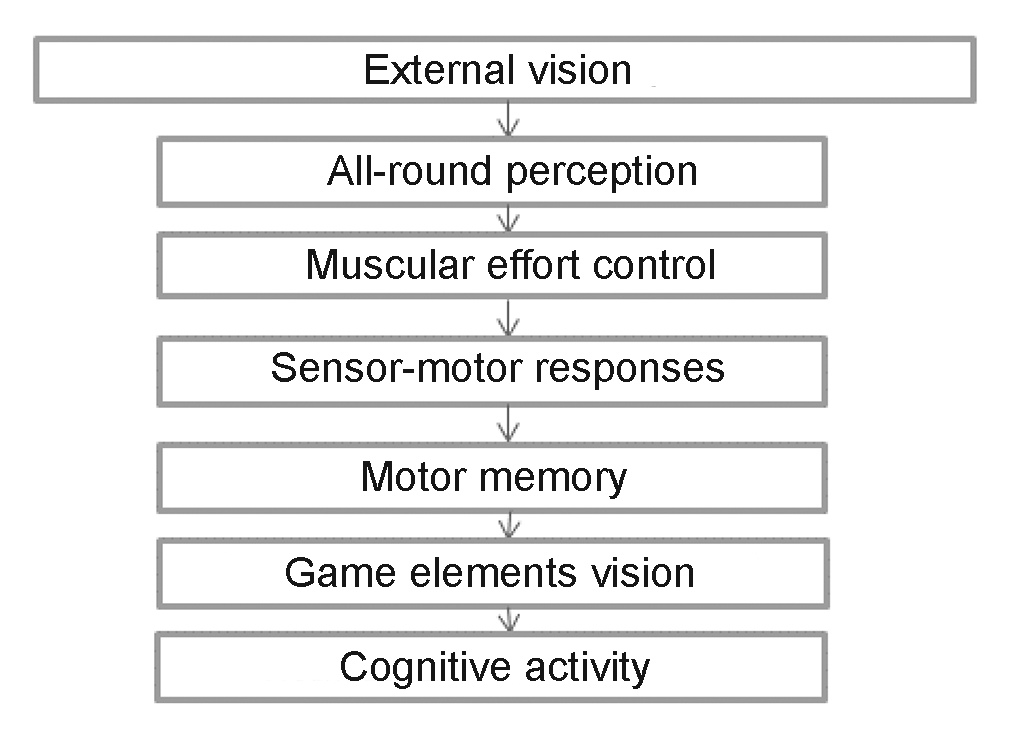
Figure 2. External vision/ orienteering qualities development process at the beginner training stage in team sports
The external vision/ orienteering training process may be described as the motor skills/ game elements mastering flow with improvements in the space/ time/ muscular effort/ sensor-motor response/ cognitive activity/ motor memory/ game elements vision aspects. The game basics mastering process cannot but be fraught with multiple errors at the beginner stage – with most of them due to the wrong perceptions of the game, immature physical fitness and underdeveloped willpower and emotional control qualities – plus the training system often being too age-unspecific. It is very important for the coach in this age period to lay a foundation for the game analyzer systems and qualities and develop the game-specific visual, kinetic, sensational, vestibular and auditory perceptions and control. Such trainings should be geared to secure progress in many game-specific qualities like the ‘feel of the field’ (with the relevant space- and pace-controls), ‘feel of the distance’, ‘feel of the ball’ etc.
It should be noted that a success of the game basics mastering process success will depend not only on the information flow in the training process but also on its processing by the individual cognitive activity – that may be ranked among the key education process success factors. The individual cognitive activity is directly correlated with the junior athlete’s motivations for good understanding of the game and, hence, the technical skills mastering process quality. These aspects of the beginner training process shall be taken into consideration by the beginner training system design and management.
Conclusion. The traditional beginner training systems in team sports give an excessive priority to the primary technical toolkit mastering at sacrifice of the game vision and tactics, and this deficiency largely hampers the beginners’ adaptation to the real game. That is why the beginner training stage in team sports shall make an emphasis on the game guiding framework development efforts, with the game technicalities naturally mastered in the actual game flow. The coach is recommended to be patient to the multiple technical errors at this stage since more important that the beginners learn to find solutions in every game situation to gradually develop a game vision. By using their still limited toolkits of game skills against the peer opponents that as unskillful as they, the junior athletes adapt their limited skills to as required by the situation-specific responses – and shall be given certain freedom to take the situation-specific solutions and handle the ball for success within their limited capacities. The more focused are the efforts to help them develop the game guiding framework at the beginner training stage, the more versatile will be their practical game experiences and more beneficial for their individual creativity and game style building, technical progress, game toolkits, tactics and teamwork for competitive success.
References
- Makarov Y.M., Churkin A.A. Didakticheskie aspekty nachalnoy takticheskoy podgotovki v sportivnykh igrakh [Didactic aspects of initial tactical training in team sports]. Study guide. St. Petersburg: Olimp publ., 2008, 119 p.
- Makarov Y.M. Soderzhanie i napravlennost pedagogicheskikh vozdeystviy na nachalnom etape podgotovki v sportivnykh igrakh [Content and focus of pedagogical effects at initial training stage in team sports]. Study guide. St. Petersburg: Olimp publ., 2009, 120 p.
- Yakhontov E.R. Didakticheskoe preobrazovanie soderzhaniya deyatelnosti sportsmena i pedagoga trenera v igrovykh vidakh sporta [Didactic transformation of the content of athlete and teacher instructor's performance in team sports]. Doct. diss. abstract (Hab.). St. Petersburg, 1995, 37 p.
Corresponding author: nataliya_lutkova@mail.ru
Abstract
Objective of the study was to develop a game basics (guiding framework) mastering training algorithm for beginners to help them acquire the primary technical/ tactical skills for success in the long-term training process. The study was designed as a part of a three-year practical trainers’ training program in team sports, with a special emphasis on the situation-specific response trainings.
The traditional beginner training systems in team sports give an excessive priority to the primary technical toolkit mastering at sacrifice of the game vision and tactics, and this deficiency largely hampers the beginners’ adaptation to the real game. The newly developed beginner training algorithm gives a special priority to the special staged goals in the long-term training process. The focused game basics mastering trainings for beginners with a special emphasis on game practices were found beneficial for the individual creativity and game style building, technical progress, game toolkits, tactics and the teamwork for competitive success. The study findings may be recommended for application in the youth training systems in team sports.


 Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE
Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE