Special health group children's mental and physical conditioning by physical education lessons
Фотографии:
ˑ:
Dr.Biol., Professor Y.A. Bukov1
N.G. Georgieva1
1Crimean Federal University, Simferopol
Keywords: education technology, integration, mental and physiological functions, special health group, physical education.
Introduction. Nowadays, schoolchildren’s mental health assessment plays an increasingly important role, since adaptive disorders have rapidly increased among children and adolescents recently. These mental states are due to the psychoemotional stress associated with anxiety emerging as a result of the child's emotional inadaptability to new social realities. Neuropsychic stress is one of the most significant and objective indicators that determine the whole complex of children’s states in future, regardless of their age [1, 2]. At the same time, it should be noted that such phenomenological indicators as anxiety level and mental stress level can serve as the markers of quality of mental health of adolescents [3]. Therefore, it is extremely important to determine the share of various forms of motor activity in the preventive and corrective after-effects of normalization of a mental state [4]. E.A. Cherepov assumes that the most adequate way to do that is to use alternative physical education means, in particular, Oriental and Occidental health-improving systems. In terms of the modern approach, the aforementioned means are viewed as part of the system of preservation and restoration of biomechanical properties of the musculoskeletal system and muscular coordination [5].
Objective of the study was to scientifically substantiate the author's education technology facilitating the integration of mental and vegetative functions of the body.
Methods and structure of the study. The research was conducted throughout the academic year and involved 14-15 year-old schoolgirls (n=96) from Simferopol attributed to the special health group. All schoolchildren were divided into two groups: Reference Group (46 girls) and Study Group (50 girls). The RG schoolchildren were engaged in the standard curriculum of the "Physical education" discipline. For the SG girls they designed and implemented into the elective course of the discipline an education technology called "Conscientious Corporeality Technology of Corporeality". "Conscientious Corporeality Technology" is based on a differentiated approach with a special emphasis on the individualized corrective and body conditioning practices with due contribution from the key concepts of the modern body conditioning therapy. The fundamental premise of the designed educational technology is a mechanism of correlation between the functional and structural changes occurring in the muscular-ligamentous apparatus and somatic health level dominated by the central nervous system [6].
The integrative correlations between the psychological and vegetative functions in terms of implementation of the educational technology were determined using the following methods: Phillips’s school anxiety test (to study the level and nature of anxiety associated with school in application to secondary schoolchildren); capnography (to evaluate the functionality of the external respiration system and determine the type of ventilation formed under the influence of psychoemotional state); other education tests to assess the schoolgirls’ physical fitness level.
Results and discussion. Both groups were characterized by similar anxiety factor values, which makes it possible to adequately evaluate further changes in the registered psychoemotional parameters during the implementation of the educational technology. In addition, it should be noted that, naturally, the level of anxiety in adolescents is evenly distributed. However, the analysis of the source materials suggests an anxiety factor imbalance. The highest degree of anxiety in the schoolgirls was associated with their fear to be worse that others expect, fear or new relationships with teachers, frustration of the need to achieve success. The lowest one - with the girls’ fear of knowledge assessment. At the same time, the overall condition index, determined by different forms of inclusion of adolescents in school life, was about 52.5%, which corresponded to increased anxiety and indicated the state of deadaptation. Under the influence of the "Conscientious Corporeality Technology", the anxiety factor values in the Study Group leveled out, with the overall downward trend, which resulted in a decrease in the baseline anxiety values by 58.8% (p<0.001). Harmonization of the schoolgirls’ psychoemotional state testifies to the generalized influence of the offered educational technology and is mandatory for enhancement of their bodily capabilities for the purpose of further improvement. There were no significant changes in the anxiety level in the Reference Group.
Since any psychoemotional tension is accompanied by an vegetative reaction, it is of particular importance to identify to which extent individual physiological systems of the body, changes in the functional indices of which can be used as stress markers, are involved in deadaptation development. Among such systems is the system of external respiration. The girls in a state of increased anxiety were found to have a tachypneic breathing pattern with changes in the even respiratory cycle, high physiological deadspace values, which is typical for shallow breathing. Rapid and shallow breathing resulted in a decrease in the level of carbon dioxide in the alveolar air, to 32.0 mmHg on the average, which is classified as hypocapnia. As demonstrated by the tests, the mental and emotional stressors are responded by hyperventilation with the relevant changes in gas homeostasis. In this context, the neurogenes-determined changes in the СО2 balance may be described as the manifestation of a disharmony in the mental and functional statuses that triggers further imbalances in the active life functionality assurance mechanisms. Introduction of the principles of body conditioning therapy into the designed educational technology led to an increase of CO2 pressure by 18.7%, (p<0.01), against the background of a decrease of the anxiety level in the schoolgirls (see Figure 1). The qualitative characteristics of the integrative correlations between the mental and vegetative functions of the body can be determined based on the correlation analysis results. The Spearman’s range correlation ratios between the anxiety factors and external respiration rates indicated that the number of correlations increases following the implementation of the educational technology. If at the beginning of the experiment we detected only three statistically significant correlations, at the end of the academic year their number increased to ten (r=0.222-0.433; p <0.05). Increasing number of correlation relationships means that the integrative functions of the body improve, which contributes to the enhancement of its adaptive resources.
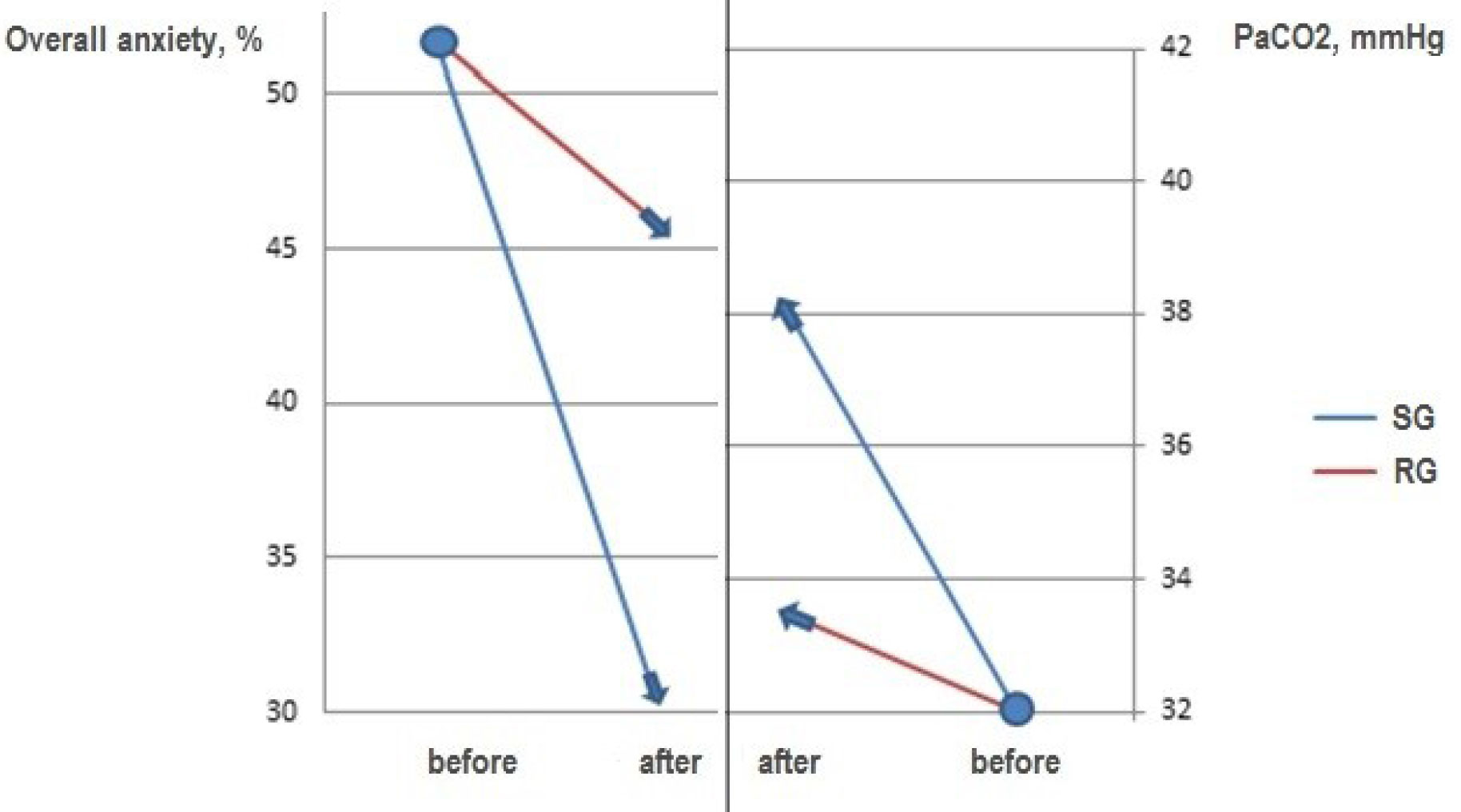
Figure 1. Dynamics of changes in indices of overall anxiety and CO2 pressure in alveolar gas in schoolgirls affected by the educational technology
Thus, integration of the mental and physiological functions into the process of motor task solution by schoolchildren learning to consciously control their muscle tone served as a background for further improvement of their physical fitness and psychosomatic health.
The participants of the experiment differed from their peers by higher strength indices in the basic muscle groups, overall endurance, coordination, speed-strength qualities and flexibility.
Conclusion. The proposed author's educational technology not only facilitates the integration of the mental and vegetative functions of the body, but also acts as an effective method of kinesiological resource building in schoolchildren.
References
- Andryushchenko L.B., Vitko S.Y. Globalnye tendentsii zdoroveformiruyuschego obraza zhizni v sisteme obrazovatelnykh organizatsiy [Global trends of health building lifestyle in the system of educational organizations]. Pedagogicheskiy opyt: teoriya, metodika, praktika, 2016, no. 4 (9), pp. 332-335.
- Bukov Y.A., Georgieva N.G. Zdorovesberegayuschie tekhnologii i metody telesno-orientirovannoy terapii na urokakh po fizicheskomu vospitaniyu uchaschikhsya spetsialnoy meditsinskoy gruppy [Health-protecting technologies and methods of bodily-oriented therapy at physical education lessons for special health group students]. Uchenye zapiski un-ta im. P.F. Lesgafta, 2015, no. 6, pp. 31-36.
- Kazantinova G.M., Charova T.A., Andryuschenko L.B. Fizicheskaya kultura studenta. Uchebnik [Student's physical culture. Textbook]. Volgograd, 2017.
- Lubysheva L.I., Zagrevskaya A.I. Integratsiya fizicheskogo i psikhicheskogo razvitiya studentov na osnove kineziologicheskogo podkhoda k ikh fizkulturno-sportivnomu obrazovaniyu [Integration of physical and mental development of students using kinesiological approach to their physical culture and sports education]. Fizicheskaya kultura: vospitanie, obrazovanie, trenirovka, 2015, no. 2, pp. 1-5.
- Nekhoroshkova A.N., Gribanova A.V., Jos Y.S. Problema trevozhnosti kak slozhnogo psikhofiziologicheskogo yavleniya [Problem of anxiety as a complex psychophysiological phenomenon]. Ekologiya cheloveka [Human Ecology], 2015, no. 6, pp. 47-54.
- Paranicheva T.M., Babenkova E.A., Tyurina E.V. Vozrastnye i polovye osobennosti psikhicheskogo zdorovya detey 10-11 let [Age and sexual characteristics of mental health of 10-11 year olds]. Novye issledovaniya, 2013, no. 4, pp.115-130.
- Chekhonin A.D. Zanyatiya vostochnymi edinoborstvami kak faktor regulyatsii psikhicheskogo napryazheniya i treovozhnosti starshego doshkolnika [Martial arts practices to control senior preschoolers' mental tension and anxiety]. Fizicheskaya kultura: vospitanie, obrazovanie, trenirovka, 2016, no. 3, pp. 37-40.
- Cherepov E.A. Sodeystvie sokhraneniyu psikhicheskogo zdorovya podrostkov v protsesse fizicheskogo vospitaniya v shkole [Promotion of mental health of adolescents in school physical education process]. Vestnik YuUrGU. Seriya ‘Obrazovanie, zdravookhranenie, fizicheskaya kultura’, 2013, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 9-16.
Corresponding author: andryushenko-lil@mail.ru
Abstract
The study analyses some issues of the special health group children’s health protection in view of the fact that high mental and emotional stresses contribute to the overall personality anxiety and may be detrimental to the students’ health. The authors offer a Conscientious Corporeality Technology of their own design making a special emphasis on the individualized corrective and body conditioning practices with due contribution from the key concepts of the modern body conditioning therapy. Subject to the study were the 14-15 year-old schoolgirls (n=96) from Simferopol attributed to the special health group. As demonstrated by the tests, the mental and emotional stressors are responded by hyperventilation with the relevant changes in gas homeostasis. The neurogenes-determined changes in the СО2 balance may be described as the manifestation of a disharmony in the mental and functional statuses that triggers further imbalances in the active life functionality assurance mechanisms. The new Conscientious Corporeality Technology is designed to secure due harmonization of the mental and vegetative functions and facilitate the kinesiological resource building process in schoolchildren.



 Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE
Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE