National physical culture and sports sector long-term development strategy
Фотографии:
ˑ:
Dr.Hab., Professor N.V. Parshikova1
Dr.Hab. S.I. Izaak2
PhD V.N. Malits1
1Ministry of Sports of the Russian Federation, Moscow
2Institute of World Civilizations, Moscow
Keywords: strategic planning, Strategy, forecasts, reference points, human resource.
Background. Strategic planning as a function of the strategic management system may be described as the process designed to create and implement a variety of programs and action plans in every sector to build up certain development strategies and attain certain strategic goals [12]. In the national physical culture and sports (PCS) sector, the strategic planning and programmatic activity is formalised by the following valid strategic planning documents: National Physical Culture and Sports Sector Development Strategy for the Period up to 2020 (Strategy); and the Federal Physical Culture and Sports Sector Priority Development Program for the Period of 2016-2020 [10].
Objective of the study was to offer a set of reference points for the National Physical Culture and Sports Sector Long-term Development Strategy and identify the key expected results of the Strategy for the period up to 2020.
Study results and discussion.
Long-term strategy: global trends. The physical culture and sports sector strategy for the nearest 15-20 years shall factor in the global and national trends. It is highly important for sustainable development of the sector that the following interrelated elements are duly harmonised for wellbeing of every individual and society on the whole: economic growth, social integration and environmental protection. As provided by the draft National Socio-Economic Long-term Development Strategy of the Russian Federation for the Period up to 2030, further growth of the global economy will be determined not only by the research and technological progress but also by the human and capital resource mobilisation opportunities [9].
Long-term strategy: national trends. Long-term strategy design process in Russia is driven by the strategic priorities dictated by the key goals of the economic, political and social reforms designed to secure sustainable national progress. As specified in the Long-term Socio-Economic Development Concept of the Russian Federation for the Period up to 2020, it is designed to “secure the sustainable growth of Russian people’s wellbeing, national security, dynamic economic growth and further consolidation of the Russian positions on the global arenas” with every upcoming challenge being addressed in the process [8]. Presently the national government takes persistent efforts for transition to the innovative, socially sensitive and competitive modern economy. The valid Innovative Development Strategy of the Russian Federation for the Period up to 2020 sets the long-term development process goals that will secure high living standards for the national population and further strengthening of the country’s geopolitical role and leadership [11]. Human being and human resource on the whole are considered a core element of the socio-economic reforms that shall provide an impetus for the long-term national development and secure the Russian leadership on the global arenas.
Long-term strategy: physical culture and sports sector. Modern national communities tend to increasingly appreciate the importance and valuable contribution of the national physical culture and sports sector to the socio-economic progress of the country [1-3]. Physical education and sports activity is commonly known to improve health, build up social activity and working capacity, promote healthy lifestyle and prevent destructive behavioural trends in the young peoples’ communities [4-7]. The priority long-term goals for the national physical culture and sports sector are set forth in the Strategy and interconnected with the priorities of the Long-term Socio-Economic Development Concept of the Russian Federation for the Period up to 2020: see Figure 1 hereunder.
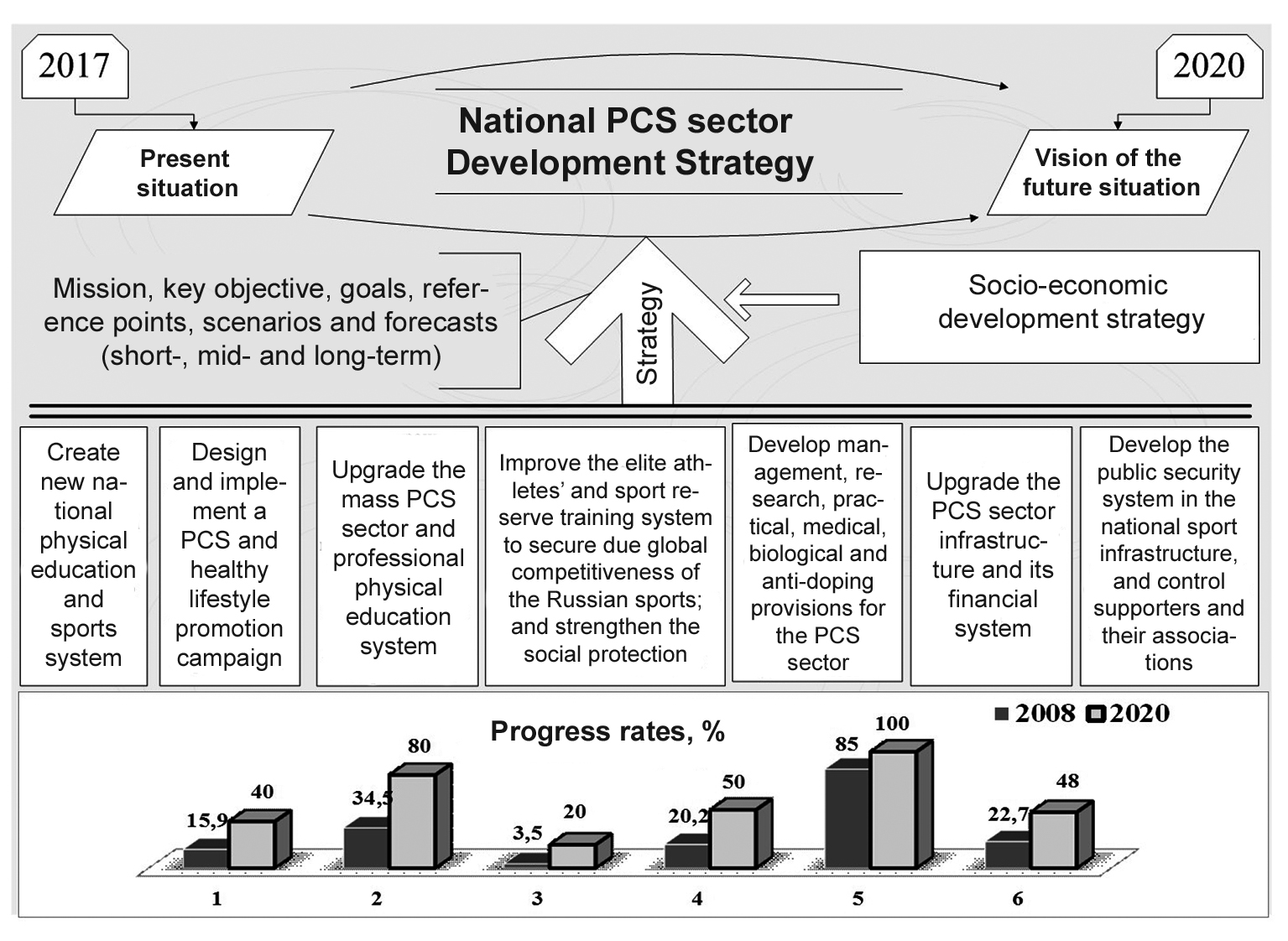
Figure 1. National physical culture and sports sector progress as provided by the Strategy
Future situation in the national physical culture and sports sector as of 2020 may be described by a set of progress rates versus the relevant goals set forth in the Strategy for 2020: see Table 1 hereunder.
Table 1. Values of the priority progress rates versus the relevant goals set in the Strategy for 2020
|
|
Progress rates |
Value |
|
|
Priority goals |
|||
|
1 |
Share of the national 3-79 year-old population engaged in habitual PCS in the total population, % |
40 |
|
|
2 |
Share of the national school and university population engaged in habitual PCS in the relevant group total, % |
80 |
|
|
3 |
Share of the national disabled and health-deficient population engaged in habitual PCS in the relevant group total, % |
20 |
|
|
4 |
Share of the national underage (6-15 year-old) population trained at special sport establishments, in the total underage population, % |
50 |
|
|
5 |
Beginners trained in winter sports according to the school sport system, thousand |
430 |
|
|
6 |
Share of the Russian national team members checked by the doping control system in the relevant group total, % |
100 |
|
|
7 |
Certified coaches and instructors employed in the national physical education and sports system and providing the certified physical education, health and sporting services, thousand |
360 |
|
|
8 |
Peak-time visitor capacity of sport facilities, % |
48 |
|
|
Expected results versus strategic goals |
|||
|
1 |
Corporate entities holding their own sport clubs, % |
45 |
|
|
2 |
Share of the population engaged in habitual PCS taking 6+ hours a week, in the total population, % |
35 |
|
|
3 |
Share of preschoolers enjoying obligatory and optional physical education services in the preschool education system, % |
100 |
|
|
4 |
Share of the SHG (special health group) school and university students enjoying special physical education services, % |
95 |
|
|
5 |
Share of the population engaged in self-reliant PCS, % |
35 |
|
|
6 |
Share of the employees engaged in hygienic gymnastics at work in the total personnel, % |
25 |
|
|
7 |
Share of military and special service personnel (%): - Rated ‘good’ and ‘excellent’ by the relevant physical fitness tests; - Having athletic title; - Engaged in leisure-time PCS taking 5+ hours a week |
90 50 100 |
|
|
8 |
Share of the population physically fit for service in the Armed Forces, special units, security services and law-enforcement bodies, in the total pre-draft-age population, % |
80 |
|
|
9 |
Share of the PCS sector personnel having professional education certificates, % |
70 |
|
It is clear that some goals and the relevant progress rates of the Strategy and the relevant provisions need to be adjusted as required by the ongoing conceptual analyses of the modern development trends in the national and global system of relationship. The National Physical Culture and Sports Sector Long-term Development Strategy for the Period up to 2030 is due to be approved by the Government of Russian Federation in 2018.
Conclusion. The key objective, interim goals, scenarios and forecasts (long-, mid- and short-term) forming a basis for the Development Strategy shall be designed with due account of the public, private business and non-governmental interests and the national human resource development agenda.
References
- Vinogradov P.A. Kontseptsiya razvitiya fizicheskoy kultury i sporta v RF na period do 2005 g. [The concept of development of physical culture and sports in the Russian Federation for the period up to 2005]. Mater. nauch.-prakt. konf. 'Razvitie fizicheskoy kultury i sporta na Dalnem Vostoke (sostoyaniya, problemy i perspektivy)' [Proc. res.-practical conf. 'Development of physical culture and sports in the Far East (conditions, problems and prospects)']. Khabarovsk: FESAPC publ., 2001, pp. 348 – 354.
- Vinogradov P.A. Fizicheskaya kultura i sport trudyaschikhsya: nauchno-metodicheskie, sotsiologicheskie i organizatsionnye aspekty [Physical culture and sports for working people: scientific-methodological, sociological and organizational aspects]. Moscow: Sovetskiy sport publ., 2015, 176 p.
- Vinogradov P.A., Dushanin A.P., Zholdak V.I. Osnovy fizicheskoy kultury i zdorovogo obraza zhizni. Ucheb. posobie dlya uchebnykh zavedeniy [Fundamentals of Physical Education and Healthy Lifestyle. Study guide for educational institutions]. Moscow: Sovetskiy sport publ., 1996, 587 p.
- Vinogradov P.A., Okunkov Y.V. Monitoring propagandy fizicheskoy kultury i sporta i zdorovogo obraza zhizni sredstvami massovoy informatsii [Monitoring of propaganda of physical culture and sports and healthy lifestyles via mass media]. Moscow: Sovetskiy sport publ., 2012, 108 p.
- Vinogradov P.A., Okunkov Y.V. O nekotorykh problemakh razvitiya veteranskogo sporta i puti ikh resheniya [Some problems of development of veteran sport and solutions]. Vestnik sportivnoy nauki, 2015, no. 2, pp. 7-9.
- Vinogradov P.A., Okunkov Y.V., Khokhlov V.I. Fizicheskaya kultura i sport v selskoy mestnosti Rossiyskoy Federatsii: sostoyanie, problemy, puti resheniya [Physical culture and sport in the rural areas of the Russian Federation: state, problems, solutions]. Moscow: Sport publ., 2015, 208 p.
- Vinogradov P.A., Savin V.A. Sport v mire informatsii [Sport in the world of information]. Teoriya i praktika fiz. kultury, 1997, no. 11, pp. 59-62.
- Kontseptsiya dolgosrochnogo sotsialno-ekonomicheskogo razvitiya Rossiyskoy Federatsii na period do 2020 g. [The concept of long-term social and economic development of the Russian Federation for the period until 2020]. Available at: http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_82134/28c7f9e359e8af09d72...( Date of access: 20.06.2017).
- Prognoz dolgosrochnogo sotsialno-ekonomicheskogo razvitiya Rossiyskoy Federatsii na period do 2030 g. [Forecast of long-term socio-economic development of the Russian Federation for the period until 2030]. Available at: http://economy.gov.ru/minec/activity/sections/macro/prognoz/doc20130325_06 (Date of access: 20.06.2017).
- Strategiya razvitiya fizicheskoy kultury i sporta v Rossiyskoy Federatsii na period do 2020 g. [Strategy of development of physical culture and sports in the Russian Federation for the period until 2020]. Available at: http://www.lipetskregionsport.ru/1114/1135.htm (Date of access: 20.06.2017).
- Strategiya innovatsionnogo razvitiya [Strategy of innovation development]. Available at: http://economy.gov.ru / minec / activity / sections/innovations/doc20120210_04 (Date of access: 20.06.2017).
- Federalny zakon no. 172-FZ ot 28.06.2014 «O strategicheskom planirovanii v Rossiyskoy Federatsii» [Federal Law no. 172-ФЗ of 28.06.2014 "On Strategic Planning in the Russian Federation"]. Available at: http://base.garant.ru/70684666/ (Date of access: 20.06.2017).
Corresponding author: sports-8@mail.ru
Abstract
Today a top priority among the objective needs of the country is given to the socio-economic development strategic planning initiatives. Objective of the study was to offer a set of reference points for the National Physical Culture and Sports Sector Long-term Development Strategy and identify the key expected results of the Strategy for the period up to 2020. We conclude that the National Physical Culture and Sports Sector Long-term Development Strategy for the Period up to 2030 shall be drafted with due consideration for the best foreign and Russian long-term strategic planning experience and documents to prudently design the progress trajectory and attain the stated goals based on due analyses of the situation and a clear vision of expected outcomes. The key objective, interim goals, scenarios and forecasts forming a basis for the Development Strategy shall be designed with due account of the public, private business and non-governmental interests and the national human resource development agenda.



 Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE
Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE